Galantamine counteracts development of learning impairment in guinea pigs exposed to the organophosphorus poison soman: clinical significance
- PMID: 21784098
- PMCID: PMC5673497
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuro.2011.07.001
Galantamine counteracts development of learning impairment in guinea pigs exposed to the organophosphorus poison soman: clinical significance
Abstract
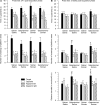
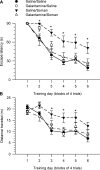
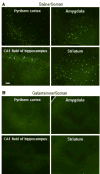
Galantamine, a drug used to treat Alzheimer's disease, protects guinea pigs against the acute toxicity and lethality of organophosphorus (OP) compounds, including soman. Here, we tested the hypothesis that a single exposure of guinea pigs to 1xLD50 soman triggers cognitive impairments that can be counteracted by galantamine. Thus, animals were injected intramuscularly with saline (0.5 ml/kg) or galantamine (8 mg/kg) and 30 min later injected subcutaneously with soman (26.3 μg/kg) or saline. Cognitive performance was analyzed in the Morris water maze (MWM) four days or three months after the soman challenge. Fifty percent of the saline-injected animals that were challenged with soman survived with mild-to-moderate signs of acute toxicity that subsided within a few hours. These animals showed no learning impairment and no memory retention deficit, when training in the MWM started four days post-soman challenge. In contrast, animals presented significant learning impairment when testing started three months post-challenge. Though the magnitude of the impairment correlated with the severity of the acute toxicity, animals that presented no or only mild signs of toxicity were also learning impaired. All guinea pigs that were treated with galantamine survived the soman challenge with no signs of acute toxicity and learned the MWM task as control animals, regardless of when testing began. Galantamine also prevented memory extinction in both saline- and soman-challenged animals. In conclusion, learning impairment develops months after a single exposure to 1xLD50 soman, and galantamine prevents both the acute toxicity and the delayed cognitive deficits triggered by this OP poison.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
The use of galantamine as an antidote against OP poisoning is protected under the International Patent Application PCT/US05/33789 filed on September 23, 2005.
The opinions or assertions contained herein are the private views of the authors and are not to be construed as reflecting the view of the National Institutes of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the Department of the Army, the Department of Defense, or the federal government.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Galantamine prevents long-lasting suppression of excitatory synaptic transmission in CA1 pyramidal neurons of soman-challenged guinea pigs.Neurotoxicology. 2014 Sep;44:270-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2014.07.005. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Neurotoxicology. 2014. PMID: 25064080 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment of Guinea pigs with galantamine prevents immediate and delayed effects of soman on inhibitory synaptic transmission in the hippocampus.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010 Sep 1;334(3):1051-8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.110.167700. Epub 2010 Jun 16. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2010. PMID: 20554906 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging reveals that galantamine prevents structural brain damage induced by an acute exposure of guinea pigs to soman.Neurotoxicology. 2010 Jan;31(1):67-76. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2009.09.004. Epub 2009 Sep 24. Neurotoxicology. 2010. PMID: 19782102
-
Stoichiometric and catalytic scavengers as protection against nerve agent toxicity: a mini review.Toxicology. 2007 Apr 20;233(1-3):31-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2006.11.066. Epub 2006 Dec 1. Toxicology. 2007. PMID: 17188793 Review.
-
An update on the pharmacology of galantamine.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007 Dec;16(12):1987-98. doi: 10.1517/13543784.16.12.1987. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2007. PMID: 18042006 Review.
Cited by
-
Prenatal exposure of guinea pigs to the organophosphorus pesticide chlorpyrifos disrupts the structural and functional integrity of the brain.Neurotoxicology. 2015 May;48:9-20. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2015.02.002. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Neurotoxicology. 2015. PMID: 25704171 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence of mild cognitive impairment in Gulf War veterans: a follow-up study.Front Neurosci. 2024 Jan 22;17:1301066. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1301066. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38318196 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial learning impairment in prepubertal guinea pigs prenatally exposed to the organophosphorus pesticide chlorpyrifos: Toxicological implications.Neurotoxicology. 2016 Sep;56:17-28. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2016.06.008. Epub 2016 Jun 11. Neurotoxicology. 2016. PMID: 27296654 Free PMC article.
-
Animal models that best reproduce the clinical manifestations of human intoxication with organophosphorus compounds.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014 Aug;350(2):313-21. doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.214932. Epub 2014 Jun 6. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014. PMID: 24907067 Free PMC article.
-
Letrozole delays acquisition of water maze task in female BALB/c mice: Possible involvement of anxiety.Horm Behav. 2024 Jun;162:105524. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2024.105524. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Horm Behav. 2024. PMID: 38513526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albuquerque EX, Deshpande SS, Kawabuchi M, Aracava Y, Idriss M, Rickett DL, Boyne AF. Multiple actions of anticholinesterase agents on chemosensitive synapses: molecular basis for prophylaxis and treatment of organophosphate poisoning. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1985;5:S182–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

