Ghrelin reduces hypertonic saline intake in a variety of natriorexigenic conditions
- PMID: 21784787
- PMCID: PMC3173603
- DOI: 10.1113/expphysiol.2011.059535
Ghrelin reduces hypertonic saline intake in a variety of natriorexigenic conditions
Abstract
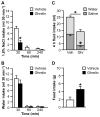
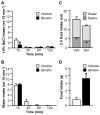
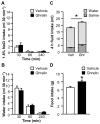
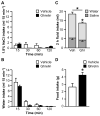
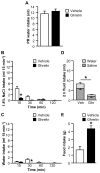
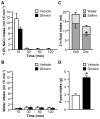
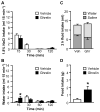
Ghrelin is a gut peptide that has been studied extensively for its role in food intake and energy balance. More recent studies show that ghrelin reduces water intake in rats and some non-mammalian species. Despite the importance of the regulation of NaCl intake in body fluid homeostasis, the effects of ghrelin on saline intake have not been investigated. Accordingly, we tested the effect of ghrelin on water and 1.8% NaCl intake in two-bottle test conditions with the following five stimuli that increase hypertonic saline intake: central angiotensin II administration; 24 h fluid deprivation; water deprivation followed by partial rehydration; dietary sodium deficiency; and polyethylene glycol administration combined with dietary sodium deficiency. We found that ghrelin attenuated saline intake stimulated by angiotensin II, by water deprivation followed by partial rehydration and by dietary sodium deficiency. We did not detect an effect of ghrelin on saline intake after 24 h fluid deprivation without partial rehydration or after the combination of polyethylene glycol and dietary sodium deficiency. The finding that ghrelin reduced hypertonic saline intake in some, but not all, natriorexigenic conditions mirrors the previously published findings that in one-bottle tests of drinking, ghrelin reduces water intake in only some conditions. The results provide evidence for a new role for ghrelin in the regulation of body fluid homeostasis.
Figures
References
-
- Buggy J, Fisher AE. Evidence for a dual central role for angiotensin in water and sodium intake. Nature. 1974;250:733–735. - PubMed
-
- Cowley MA, Smith RG, Diano S, Tschop M, Pronchuk N, Grove KL, Strasburger CJ, Bidlingmaier M, Esterman M, Heiman ML, Garcia-Segura LM, Nillni EA, Mendez P, Low MJ, Sotonyi P, Friedman JM, Liu H, Pinto S, Colmers WF, Cone RD, Horvath TL. The distribution and mechanism of action of ghrelin in the CNS demonstrates a novel hypothalamic circuit regulating energy homeostasis. Neuron. 2003;37:649–661. - PubMed
-
- Cummings DE, Purnell JQ, Frayo RS, Schmidova K, Wisse BE, Weigle DS. A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes. 2001;50:1714–1719. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

