Effect of phosphate binders on serum inflammatory profile, soluble CD14, and endotoxin levels in hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 21784820
- PMCID: PMC3359006
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.01650211
Effect of phosphate binders on serum inflammatory profile, soluble CD14, and endotoxin levels in hemodialysis patients
Abstract
Background and objectives: Hyperphosphatemia and subclinical endotoxemia are important sources of inflammation in HD. Proinflammatory cytokines are strong correlates of soluble CD14 (sCD14) concentrations, an independent predictor of mortality in this population. We evaluated the effects of calcium acetate and sevelamer hydrochloride on serum inflammatory profile, endotoxin concentrations, and sCD14 levels in HD patients.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Prospective, randomized, open-label, parallel design trial. Fifty-nine stable HD patients, 30 receiving sevelamer, and 29 receiving calcium acetate were evaluated. Serum levels of inflammatory parameters (high-sensitivity C-reactive protein [hs-CRP], TNF-α, interleukin (IL)-1, -6, -10, and -18), as well as endotoxin and sCD14 concentrations, were measured at baseline and after 3 months of therapy.
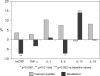
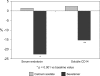
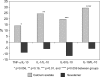
Results: Serum IL-6 increased in patients receiving calcium acetate, whereas hs-CRP and IL-6 significantly decreased in subjects treated with sevelamer, with IL-10 experiencing a trend to increase (P = 0.052). Serum endotoxin and sCD14 levels did not change after treatment with calcium acetate. However, these parameters decreased by 22.6% and 15.2%, respectively (P < 0.01), in patients receiving sevelamer. Multiple regression analysis showed that variation in serum endotoxin concentrations was the strongest factor associated with IL-6 change, whereas the only variables independently associated with changes in sCD14 levels were the variations in serum IL-6 and endotoxin concentrations.
Conclusions: Administration of the noncalcium phosphate binder sevelamer to maintenance HD patients is associated with a significant decrease in hs-CRP, IL-6, serum endotoxin levels and sCD14 concentrations.
Figures
References
-
- Stenvinkel P, Ketteler M, Johnson RJ, Lindholm B, Pecoits-Filho R, Riella M, Heimburger O, Cederholm T, Girndt M: IL-10, IL-6, and TNF-a: Central factors in the altered cytokine network of uremia—The good, the bad, and the ugly. Kidney Int 67: 1216–1233, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Zimmermann J, Herrlinger S, Pruy A, Metzger T, Wanner C: Inflammation enhances cardiovascular risk and mortality in hemodialysis. Kidney Int 55: 648–658, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Stenvinkel P: Inflammation in end-stage renal disease: The hidden enemy. Nephrology (Carlton) 11: 36–41, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Jofré R, Rodríguez-Benítez P, López-Gómez JM, Pérez-García R: Inflammatory syndrome in patients on hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol 17: S274–S280, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Sundaram S, Barrett TW, Meyer KB, Perella C, Neto MC, King AJ, Pereira BJ: Transmembrane passage of cytokine-inducing bacterial products across new and reprocessed polysulfone dialyzers. J Am Soc Nephrol 7: 2183–2191, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

