Isolation of generalized transducing bacteriophages for uropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli
- PMID: 21784916
- PMCID: PMC3187168
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.05307-11
Isolation of generalized transducing bacteriophages for uropathogenic strains of Escherichia coli
Abstract
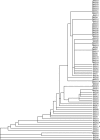
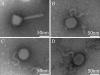
The traditional genetic procedure for random or site-specific mutagenesis in Escherichia coli K-12 involves mutagenesis, isolation of mutants, and transduction of the mutation into a clean genetic background. The transduction step reduces the likelihood of complications due to secondary mutations. Though well established, this protocol is not tenable for many pathogenic E. coli strains, such as uropathogenic strain CFT073, because it is resistant to known K-12 transducing bacteriophages, such as P1. CFT073 mutants generated via a technique such as lambda Red mutagenesis may contain unknown secondary mutations. Here we describe the isolation and characterization of transducing bacteriophages for CFT073. Seventy-seven phage isolates were acquired from effluent water samples collected from a wastewater treatment plant in Madison, WI. The phages were differentiated by a host sensitivity-typing scheme with a panel of E. coli strains from the ECOR collection and clinical uropathogenic isolates. We found 49 unique phage isolates. These were then examined for their ability to transduce antibiotic resistance gene insertions at multiple loci between different mutant strains of CFT073. We identified 4 different phages capable of CFT073 generalized transduction. These phages also plaque on the model uropathogenic E. coli strains 536, UTI89, and NU14. The highest-efficiency transducing phage, ΦEB49, was further characterized by DNA sequence analysis, revealing a double-stranded genome 47,180 bp in length and showing similarity to other sequenced phages. When combined with a technique like lambda Red mutagenesis, the newly characterized transducing phages provide a significant development in the genetic tools available for the study of uropathogenic E. coli.
Figures


References
-
- Bahrani-Mougeot F. K., et al. 2002. Type 1 fimbriae and extracellular polysaccharides are preeminent uropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence determinants in the murine urinary tract. Mol. Microbiol. 45:1079–1093 - PubMed
-
- Chandra K., Kidwai J. R., Gupta B. M. 1979. Morphology, serology and biochemical characters of phage CVX-5, isolated from a patient with colitis. Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 24:334–338 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

