Regulation of the virulence determinant OspC by bbd18 on linear plasmid lp17 of Borrelia burgdorferi
- PMID: 21784941
- PMCID: PMC3187453
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01496-10
Regulation of the virulence determinant OspC by bbd18 on linear plasmid lp17 of Borrelia burgdorferi
Abstract
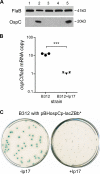
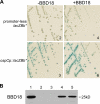
Persistent infection of a mammalian host by Borrelia burgdorferi, the spirochete that causes Lyme disease, requires specific downregulation of an immunogenic outer surface protein, OspC. Although OspC is an essential virulence factor needed by the spirochete to establish infection in the mammal, it represents a potent target for the host acquired immune response, and constitutive expression of OspC results in spirochete clearance. In this study, we demonstrate that a factor encoded on a linear plasmid of B. burgdorferi, lp17, can negatively regulate ospC transcription from the endogenous gene on the circular plasmid cp26 and from an ospC promoter-lacZ fusion on a shuttle vector. Furthermore, we have identified bbd18 as the gene on lp17 that is responsible for this effect. These data identify a novel component of ospC regulation and provide the basis for determining the molecular mechanisms of ospC repression in vivo.
Figures

References
-
- Beaurepaire C., Chaconas G. 2005. Mapping of essential replication functions of the linear plasmid lp17 of Borrelia burgdorferi by targeted deletion walking. Mol. Microbiol. 57:132–142 - PubMed
-
- Benach J. L., et al. 1983. Spirochetes isolated from the blood of two patients with Lyme disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 308:740–742 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

