Contributions of counter-charge in a potassium channel voltage-sensor domain
- PMID: 21785425
- PMCID: PMC4933587
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.622
Contributions of counter-charge in a potassium channel voltage-sensor domain
Abstract
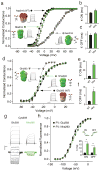
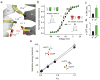
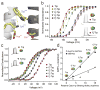
Voltage-sensor domains couple membrane potential to conformational changes in voltage-gated ion channels and phosphatases. Highly coevolved acidic and aromatic side chains assist the transfer of cationic side chains across the transmembrane electric field during voltage sensing. We investigated the functional contribution of negative electrostatic potentials from these residues to channel gating and voltage sensing with unnatural amino acid mutagenesis, electrophysiology, voltage-clamp fluorometry and ab initio calculations. The data show that neutralization of two conserved acidic side chains in transmembrane segments S2 and S3, namely Glu293 and Asp316 in Shaker potassium channels, has little functional effect on conductance-voltage relationships, although Glu293 appears to catalyze S4 movement. Our results suggest that neither Glu293 nor Asp316 engages in electrostatic state-dependent charge-charge interactions with S4, likely because they occupy, and possibly help create, a water-filled vestibule.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests as defined by Nature Publishing Group, or other interests that might be perceived to influence the results and/or discussion reported in this paper.
Figures

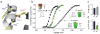
References
-
- Hille B. Ion channels of excitable membranes. 3. Sinauer; 2001.
-
- Murata Y, Iwasaki H, Sasaki M, Inaba K, Okamura Y. Phosphoinositide phosphatase activity coupled to an intrinsic voltage sensor. Nature. 2005;435:1239–1243. - PubMed
-
- Ahern CA, Horn R. Focused electric field across the voltage sensor of potassium channels. Neuron. 2005;48:25–29. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal SK, MacKinnon R. Contribution of the S4 segment to gating charge in the Shaker K+ channel. Neuron. 1996;16:1169–1177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

