Poly(amidoamine)-Cholesterol Conjugate Nanoparticles Obtained by Electrospraying as Novel Tamoxifen Delivery System
- PMID: 21785731
- PMCID: PMC3138208
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/587604
Poly(amidoamine)-Cholesterol Conjugate Nanoparticles Obtained by Electrospraying as Novel Tamoxifen Delivery System
Abstract
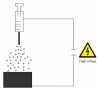
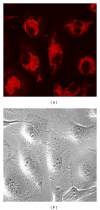
A new poly(amidoamine)-cholesterol (PAA-cholesterol) conjugate was synthesized, characterized and used to produce nanoparticles by the electrospraying technique. The electrospraying is a method of liquid atomization that consists in the dispersion of a solution into small charged droplets by an electric field. Tuning the electrospraying process parameters spherical PAA-chol nanoparticles formed. The PAA-cholesterol nanoparticles showed sizes lower than 500 nm and spherical shape. The drug incorporation capacity was investigated using tamoxifen, a lipophilic anticancer drug, as model drug. The incorporation of the tamoxifen did not affect the shape and sizes of nanoparticles showing a drug loading of 40%. Tamoxifen-loaded nanoparticles exhibited a higher dose-dependent cytotoxicity than free tamoxifen, while blank nanoparticles did not show any cytotoxic effect at the same concentrations. The electrospray technique might be proposed to produce tamoxifen-loaded PAA-chol nanoparticle in powder form without any excipient in a single step.
Figures








References
-
- Cismaru L, Popa M. Polymeric nanoparticles with biomedical applications. Revue Roumaine de Chimie. 2010;55(8):433–442.
-
- Chan JM, Valencia PM, Zhang L, Langer R, Farokhzad OC. Polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery. Methods in Molecular Biology. 2010;624:163–175. - PubMed
-
- Chauvierre C, Vauthier C, Labarre D, Couvreur P, Marden MC, Leclerc L. A new generation of polymer nanoparticles for drug delivery. Cellular and Molecular Biology. 2004;50(3):233–239. - PubMed
-
- Jayasinghe SN, Sullivan AC. Electrohydrodynamic atomization: an approach to growing continuous self-supporting polymeric fibers. Journal of Physical Chemistry B. 2006;110(6):2522–2528. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

