Assortment of GABAergic plasticity in the cortical interneuron melting pot
- PMID: 21785736
- PMCID: PMC3139185
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/976856
Assortment of GABAergic plasticity in the cortical interneuron melting pot
Abstract
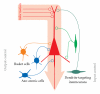
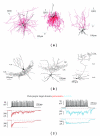
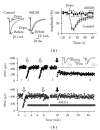
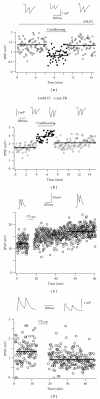
Cortical structures of the adult mammalian brain are characterized by a spectacular diversity of inhibitory interneurons, which use GABA as neurotransmitter. GABAergic neurotransmission is fundamental for integrating and filtering incoming information and dictating postsynaptic neuronal spike timing, therefore providing a tight temporal code used by each neuron, or ensemble of neurons, to perform sophisticated computational operations. However, the heterogeneity of cortical GABAergic cells is associated to equally diverse properties governing intrinsic excitability as well as strength, dynamic range, spatial extent, anatomical localization, and molecular components of inhibitory synaptic connections that they form with pyramidal neurons. Recent studies showed that similarly to their excitatory (glutamatergic) counterparts, also inhibitory synapses can undergo activity-dependent changes in their strength. Here, some aspects related to plasticity and modulation of adult cortical and hippocampal GABAergic synaptic transmission will be reviewed, aiming at providing a fresh perspective towards the elucidation of the role played by specific cellular elements of cortical microcircuits during both physiological and pathological operations.
Figures
References
-
- Buzsáki G, Draguhn A. Neuronal olscillations in cortical networks. Science. 2004;304(5679):1926–1929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

