Therapeutic target achievement in type 2 diabetic patients after hyperglycemia, hypertension, dyslipidemia management
- PMID: 21785747
- PMCID: PMC3138102
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2011.35.3.264
Therapeutic target achievement in type 2 diabetic patients after hyperglycemia, hypertension, dyslipidemia management
Abstract
Background: Our study group established "3H care" in 2002. The meaning of "3H care" attain and maintain adequate controls over hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetic patients. This study evaluated the achievement of target goals after one year or more of "3H care" by specialists in our diabetic clinic.
Methods: This was a retrospective study of 200 type 2 diabetic patients who received "3H care" for one year or more in our diabetic clinic. We evaluated achievement of target goals for metabolic controls as suggested by the American Diabetes Association.
Results: Overall, 200 type 2 diabetes patients were enrolled, of whom 106 were males (53%) and 94 were females (47%). After one year of "3H care," the mean HbA1c was 7.2±1.5% and the percentage of patients achieving glycemic control (HbA1c <7%) was 51.8%. However only 32.2% of hypertensive patients achieved the recommended target. After one year of "3H care," the percentages of those who achieved the target value for dyslipidemia were 80.0% for total cholesterol, 66.3% for low density lipoprotein cholesterol, 57.9% for triglyceride, and 51.8% for high density lipoprotein cholesterol. The percentage that achieved all three targets level was only 4.4% after one year and 14.8% after two years.
Conclusion: The results of this study demonstrate that only a minor proportion of patients with type 2 diabetes achieved the recommended goals despite the implementation of "3H care." It is our suggestion that better treatment strategies and methods should be used to control hypertension, hyperlipidemia and hyperglycemia.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus, type 2; Disease management; Treatment outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
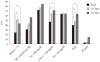
References
-
- Savage PJ. Cardiovascular complications of diabetes mellitus: what we know and what we need to know about their prevention. Ann Intern Med. 1996;124(1 Pt 2):123–126. - PubMed
-
- Barrett-Connor EL, Cohn BA, Wingard DL, Edelstein SL The Rancho Bernardo Study. Why is diabetes mellitus a stronger risk factor for fatal ischemic heart disease in women than in men? JAMA. 1991;265:627–631. - PubMed
-
- Haffner SM, Lehto S, Ronnemaa T, Pyorala K, Laakso M. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:229–234. - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB, McGee DL. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The Framingham study. JAMA. 1979;241:2035–2038. - PubMed
-
- Comaschi M, Coscelli C, Cucinotta D, Malini P, Manzato E, Nicolucci A SFIDA Study Group--Italian Association of Diabetologists (AMD) Cardiovascular risk factors and metabolic control in type 2 diabetic subjects attending outpatient clinics in Italy: the SFIDA (survey of risk factors in Italian diabetic subjects by AMD) study. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2005;15:204–211. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

