Liraglutide prevents hypoadiponectinemia-induced insulin resistance and alterations of gene expression involved in glucose and lipid metabolism
- PMID: 21785811
- PMCID: PMC3321815
- DOI: 10.2119/molmed.2011.00051
Liraglutide prevents hypoadiponectinemia-induced insulin resistance and alterations of gene expression involved in glucose and lipid metabolism
Abstract
Liraglutide is a glucagonlike peptide (GLP)-1 analog that reduces blood glucose levels, increases insulin secretion and improves insulin sensitivity through mechanisms that are not completely understood. Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the metabolic impact and underlying mechanisms of liraglutide in a hypoadiponectinemia and high-fat diet (HFD)-induced insulin resistance (IR) model. Adiponectin gene targeting was achieved using adenovirus-transduced RNAi and was used to lower plasma adiponectin levels. Liraglutide (1 mg/kg) was given twice daily for 8 wks to HFD-fed apolipoprotein (Apo)E⁻/⁻ mice. Insulin sensitivity was examined by a hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp. Gene mRNA and protein expressions were measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and Western blot, respectively. Administration of liraglutide prevented hypoadiponectinemia-induced increases in plasma insulin, free fatty acids, triglycerides and total cholesterol. Liraglutide also attenuated hypoadiponectinemia-induced deterioration in peripheral and hepatic insulin sensitivity and alterations in key regulatory factors implicated in glucose and lipid metabolism. These findings demonstrated for the first time that liraglutide could be used to rescue IR induced by hypoadiponectinemia and HFD via regulating gene and protein expression involved in glucose and lipid metabolism.
Figures



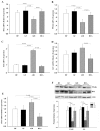

References
-
- Kieffer TJ, Habener JF. The glucagon-like peptides. Endocr Rev. 1999;20:876–913. - PubMed
-
- Agerso H, Vicini P. Pharmacodynamics of NN2211, a novel long acting GLP-1 derivative. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2003;19:141–50. - PubMed
-
- Holst JJ, Orskov C, Nielsen OV, Schwartz TW. Truncated glucagon-like peptide I, an insulin-releasing hormone from the distal gut. FEBS Lett. 1987;211:169–74. - PubMed
-
- Kreymann B, Williams G, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR. Glucagonlike peptide-1-7–36: a physiological incretin in man. Lancet. 1987;2:1300–4. - PubMed
-
- Wettergren A, et al. Truncated GLP-1 (proglucagon 78-107-amide) inhibits gastric and pancreatic functions in man. Dig Dis Sci. 1993;38:665–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

