Integration of the brief behavioral activation treatment for depression (BATD) into a college orientation program: depression and alcohol outcomes
- PMID: 21787070
- PMCID: PMC4104126
- DOI: 10.1037/a0024634
Integration of the brief behavioral activation treatment for depression (BATD) into a college orientation program: depression and alcohol outcomes
Abstract
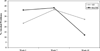
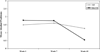
College freshmen face a variety of academic and social challenges as they adjust to college life that can place them at risk for a number of negative outcomes, including depression and alcohol-related problems. Orientation classes that focus on teaching incoming students how to better cope with college-oriented stress may provide an opportunity to prevent the development of these adjustment problems. This article outlines a program based on behavioral activation that can be integrated into college orientation programs to provide a more comprehensive orientation experience. Data are presented from an initial pilot study in which 71 first-semester freshman at the University of Maryland participated in a 15-week, 2 hr per week orientation class (n = 37 in the behavioral activation-enhanced orientation classes and n = 34 in the control orientation as usual classes). Students' depression and alcohol use were evaluated at the beginning, middle, and end of the course. Results indicated a Time × Group interaction such that problem drinking (but not consumption) was significantly reduced across assessments in the behavioral activation classes and largely unchanged in the standard classes. No difference was observed in depression scores; however, fairly low depression scores across the 3 time points may have limited the opportunity to observe any meaningful impact of the orientation classes on depression. The authors conclude with a discussion of the implications of their findings for preventing adjustment problems among incoming college students and future directions.
Figures
References
-
- Adams CE, Nagoshi CT. Changes over one semester in drinking game playing and alcohol use and problems in a college student sample. Substance Abuse. 1999;20:97–106. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Assocation. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4th ed. Washington, DC: Author; 1994.
-
- Babor TF, Higgins-Biddle JC, Saunders JB, Monteiro M. AUDIT: The Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test: Guidelines for use in primary care. Geneva, Switzerland: Department of Mental Health and Substance Dependence, World Health Organization; 2006.
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA. Beck Depression Inventory: Manual. San Antonio, TX: The Psychiatric Corporation; 1987.
-
- Benton SA, Robertson JM, Tseng W, Newton FB, Benton SL. Changes in counseling center client problems across 13 years. Professional Psychology: Research and Practice. 2003;34:66–72.

