Defining genome maintenance pathways using functional genomic approaches
- PMID: 21787120
- PMCID: PMC3144553
- DOI: 10.3109/10409238.2011.588938
Defining genome maintenance pathways using functional genomic approaches
Abstract
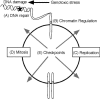
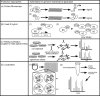
Genome maintenance activities including DNA repair, cell division cycle control, and checkpoint signaling pathways preserve genome integrity and prevent disease. Defects in these pathways cause birth defects, neurodegeneration, premature aging, and cancer. Recent technical advances in functional genomic approaches such as expression profiling, proteomics, and RNA interference (RNAi) technologies have rapidly expanded our knowledge of the proteins that work in these pathways. In this review, we examine the use of these high-throughput methodologies in higher eukaryotic organisms for the interrogation of genome maintenance activities.
Figures

References
-
- Amundson SA, Bittner M, Fornace AJ., Jr. Functional genomics as a window on radiation stress signaling. Oncogene. 2003;22:5828–33. - PubMed
-
- Baryshnikova A, Costanzo M, Dixon S, Vizeacoumar FJ, Myers CL, Andrews B, Boone C. Synthetic genetic array (SGA) analysis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Methods Enzymol. 2010;470:145–79. - PubMed
-
- Bell SP, Dutta A. DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 2002;71:333–74. - PubMed
-
- Bennett CB, Lewis LK, Karthikeyan G, Lobachev KS, Jin YH, Sterling JF, Snipe JR, Resnick MA. Genes required for ionizing radiation resistance in yeast. Nat Genet. 2001;29:426–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
