Endotoxin-free purification for the isolation of bovine viral diarrhoea virus E2 protein from insoluble inclusion body aggregates
- PMID: 21787435
- PMCID: PMC3160874
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2859-10-57
Endotoxin-free purification for the isolation of bovine viral diarrhoea virus E2 protein from insoluble inclusion body aggregates
Abstract
Background: Protein expression in Escherichia coli may result in the recombinant protein being expressed as insoluble inclusion bodies. In addition, proteins purified from E. coli contain endotoxins which need to be removed for in vivo applications. The structural protein, E2, from Bovine Viral Diarrhoea Virus (BVDV) is a major immunogenic determinant, and is an ideal candidate as a subunit vaccine. The E2 protein contains 17 cysteine residues creating difficulties in E. coli expression. In this report we outline a procedure for successfully producing soluble and endotoxin-free BVDV E2 protein from inclusion bodies (IB).
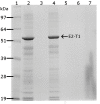
Results: The expression of a truncated form of BVDV-E2 protein (E2-T1) in E. coli resulted in predominantly aggregated insoluble IB. Solubilisation of E2-T1 with high purity and stability from IB aggregates was achieved using a strong reducing buffer containing 100 mM Dithiothreitol. Refolding by dialysis into 50 mM Tris (pH 7.0) containing 0.2% Igepal CA630 resulted in a soluble but aggregated protein solution. The novel application of a two-phase extraction of inclusion body preparations with Triton X-114 reduced endotoxin in solubilised E2-T1 to levels suitable for in vivo use without affecting protein yields. Dynamic light scattering analyses showed 37.5% of the protein was monomeric, the remaining comprised of soluble aggregates. Mice immunised with E2-T1 developed a high titre antibody response by ELISA. Western hybridisation analysis showed E2-T1 was recognised by sera from immunised mice and also by several BVDV-E2 polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies.
Conclusion: We have developed a procedure using E. coli to produce soluble E2-T1 protein from IB, and due to their insoluble nature we utilised a novel approach using Triton X-114 to efficiently remove endotoxin. The resultant protein is immunogenic and detectable by BVDV-E2 specific antibodies indicating its usefulness for diagnostic applications and as a subunit vaccine. The optimised E. coli expression system for E2-T1 combined with methodologies for solubilisation, refolding and integrated endotoxin removal presented in this study should prove useful for other vaccine applications.
Figures

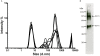
References
-
- Thiel HJ, Collett MS, Gould EA, Heinz FX, Houghton M, Meyers G, Purcell RH, Rice CM. In: Virus Taxonomy Eighth Report on the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses. Fauquet CM, Mayo MA, Maniloff J, Desselberger U, Ball LA, editor. Amsterdam: Academic Press; 2005. Family Flaviviridae; pp. 981–998.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

