Extended-spectrum AmpC cephalosporinase in Acinetobacter baumannii: ADC-56 confers resistance to cefepime
- PMID: 21788456
- PMCID: PMC3186995
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00704-11
Extended-spectrum AmpC cephalosporinase in Acinetobacter baumannii: ADC-56 confers resistance to cefepime
Abstract
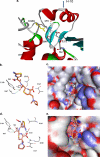
ADC-56, a novel extended-spectrum AmpC (ESAC) β-lactamase, was identified in an Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolate. ADC-56 possessed an R148Q change compared with its putative progenitor, ADC-30, which enabled it to hydrolyze cefepime. Molecular modeling suggested that R148 interacted with Q267, E272, and I291 through a hydrogen bond network which constrained the H-10 helix. This permitted cefepime to undergo conformational changes in the active site, with the carboxyl interacting with R340, likely allowing for better binding and turnover.
Figures
References
-
- Arnold K., et al. 2006. The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 22:195–201 - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute 2010. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, 20th informational supplement. CLSI, Wayne, PA
-
- Diller D. J., et al. 2001. High throughput docking for library design and library prioritization. Proteins 43:113–124 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- GDB/JF265067
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

