Role of inflammation in bladder function and interstitial cystitis
- PMID: 21789096
- PMCID: PMC3126088
- DOI: 10.1177/1756287211398255
Role of inflammation in bladder function and interstitial cystitis
Abstract
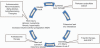
Cystitis, or inflammation of the bladder, has a direct effect on bladder function. Interstitial cystitis is a syndrome characterized by urinary bladder pain and irritative symptoms of more than 6 months duration. It commonly occurs in young to middle-aged women with no known cause and in fact represents a diagnosis of exclusion. Many factors have been suggested, including chronic or subclinical infection, autoimmunity and genetic susceptibility, which could be responsible for initiating the inflammatory response. However, a central role of inflammation has been confirmed in the pathogenesis of interstitial cystitis. Patients with interstitial cystitis are usually managed with multimodal therapy to break the vicious cycle of chronic inflammation at every step. Patients who develop irreversible pathologies such as fibrosis are managed surgically, which is usually reserved for refractory cases.
Keywords: bladder; inflammation; interstitial cystitis; management; painful bladder syndrome.
Figures


References
-
- Aaron L.A., Buchwald D. (2001) A review of the evidence for overlap among unexplained clinical conditions. Ann Intern Med 134: 868–881 - PubMed
-
- Aaron L.A., Buchwald D. (2003) Chronic diffuse musculoskeletal pain, fibromyalgia and co-morbid unexplained clinical conditions. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 17: 563–574 - PubMed
-
- Abrams P., Baranowski A., Berger R.E., Fall M., Hanno P., Wesselmann U. (2006) A new classification is needed for pelvic pain syndromes–are existing terminologies of spurious diagnostic authority bad for patients? J Urol 175: 1989–1990 - PubMed
-
- Abrams P., Cardozo L., Fall M., Griffiths D., Rosier P., Ulmsten U., et al. (2002) The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol Urodyn 21: 167–178 - PubMed
-
- Acar D., Cayan S., Aktas S., Tek M., Akbay E. (2007) The effect of tamoxifen on bladder functions and histology, and the role of estrogen receptor beta in a rat chemical cystitis model. Neurourol Urodyn 26: 309–316 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

