CBP/p300 and SIRT1 are involved in transcriptional regulation of S-phase specific histone genes
- PMID: 21789216
- PMCID: PMC3137613
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022088
CBP/p300 and SIRT1 are involved in transcriptional regulation of S-phase specific histone genes
Abstract
Background: Histones constitute a type of essential nuclear proteins important for chromatin structure and functions. The expression of major histones is strictly confined to the S phase of a cell cycle and tightly coupled to DNA replication.
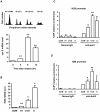
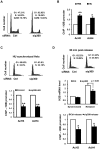
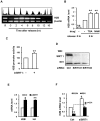
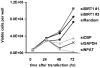
Methodology/principal findings: With RT-qPCR and ChIP assays, we investigated transcriptional regulation of the S-phase specific histone genes and found that the acetylation level of histones on core histone gene promoters fluctuated during cell cycle in a pattern similar to RNA polymerase II association. Further, we showed that CBP/p300 and SIRT1 were recruited to histone gene promoters in an NPAT-dependent manner, knockdown of which affected histone acetylation on histone gene promoters and histone gene transcription.
Significance: These observations contribute to further understanding of the mechanism by which the expression of canonical histone genes is regulated, and also implicate a link between histone expression and DNA damage repair and cell metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






Similar articles
-
Adenovirus E1A Activation Domain Regulates H3 Acetylation Affecting Varied Steps in Transcription at Different Viral Promoters.J Virol. 2018 Aug 29;92(18):e00805-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00805-18. Print 2018 Sep 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29976669 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct roles for CBP and p300 on the RA-mediated expression of the meiosis commitment gene Stra8 in mouse embryonic stem cells.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 13;8(6):e66076. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066076. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23785470 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional activation of histone genes requires NPAT-dependent recruitment of TRRAP-Tip60 complex to histone promoters during the G1/S phase transition.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jan;28(1):435-47. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00607-07. Epub 2007 Oct 29. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 17967892 Free PMC article.
-
E2F1 acetylation directs p300/CBP-mediated histone acetylation at DNA double-strand breaks to facilitate repair.Nat Commun. 2019 Oct 30;10(1):4951. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12861-8. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31666529 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic occupancy of the transcriptional co-activators p300 and CBP.Transcription. 2013 Jan-Feb;4(1):18-23. doi: 10.4161/trns.22601. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Transcription. 2013. PMID: 23131664 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Histone H2B-IFI16 Recognition of Nuclear Herpesviral Genome Induces Cytoplasmic Interferon-β Responses.PLoS Pathog. 2016 Oct 20;12(10):e1005967. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005967. eCollection 2016 Oct. PLoS Pathog. 2016. PMID: 27764250 Free PMC article.
-
FUS/TLS contributes to replication-dependent histone gene expression by interaction with U7 snRNPs and histone-specific transcription factors.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Nov 16;43(20):9711-28. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv794. Epub 2015 Aug 6. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26250115 Free PMC article.
-
Multilayered chromatin analysis reveals E2f, Smad and Zfx as transcriptional regulators of histones.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013 Jan;20(1):119-26. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2448. Epub 2012 Dec 9. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23222641
-
miR-181a-regulated pathways in T-cell differentiation and aging.Immun Ageing. 2021 Jun 15;18(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12979-021-00240-1. Immun Ageing. 2021. PMID: 34130717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNAi screening identifies KAT8 as a key molecule important for cancer cell survival.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013 Apr 15;6(5):870-7. Print 2013. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23638218 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albig W, Doenecke D. The human histone gene cluster at the D6S105 locus. Hum Genet. 1997;101:284–294. - PubMed
-
- Osley MA. The regulation of histone synthesis in the cell cycle. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:827–861. - PubMed
-
- Han M, Chang M, Kim UJ, Grunstein M. Histone H2B repression causes cell-cycle-specific arrest in yeast: effects on chromosomal segregation, replication, and transcription. Cell. 1987;48:589–597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

