Claudin-7 is frequently overexpressed in ovarian cancer and promotes invasion
- PMID: 21789222
- PMCID: PMC3137611
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022119
Claudin-7 is frequently overexpressed in ovarian cancer and promotes invasion
Abstract
Background: Claudins are tight junction proteins that are involved in tight junction formation and function. Previous studies have shown that claudin-7 is frequently upregulated in epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) along with claudin-3 and claudin-4. Here, we investigate in detail the expression patterns of claudin-7, as well as its possible functions in EOC.
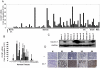
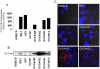
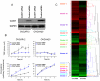
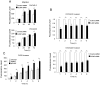
Methodology/principal findings: A total of 95 ovarian tissue samples (7 normal ovarian tissues, 65 serous carcinomas, 11 clear cell carcinomas, 8 endometrioid carcinomas and 4 mucinous carcinomas) were studied for claudin-7 expression. In real-time RT-PCR analysis, the gene for claudin-7, CLDN7, was found to be upregulated in all the tumor tissue samples studied. Similarly, immunohistochemical analysis and western blotting showed that claudin-7 protein was significantly overexpressed in the vast majority of EOCs. Small interfering RNA-mediated knockdown of claudin-7 in ovarian cancer cells led to significant changes in gene expression as measured by microarrays and validated by RT-PCR and immunoblotting. Analyses of the genes differentially expressed revealed that the genes altered in response to claudin-7 knockdown were associated with pathways implicated in various molecular and cellular functions such as cell cycle, cellular growth and proliferation, cell death, development, and cell movement. Through functional experiments in vitro, we found that both migration and invasion were altered in cells where CLDN7 had been knocked down or overexpressed. Interestingly, claudin-7 expression was associated with a net increase in invasion, but also with a decrease in migration.
Conclusion/significance: Our work shows that claudin-7 is significantly upregulated in EOC and that it may be functionally involved in ovarian carcinoma invasion. CLDN7 may therefore represent potential marker for ovarian cancer detection and a target for therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Tight junction proteins claudin-3 and claudin-4 are frequently overexpressed in ovarian cancer but not in ovarian cystadenomas.Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Jul;9(7):2567-75. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12855632
-
Suppression of the grainyhead transcription factor 2 gene (GRHL2) inhibits the proliferation, migration, invasion and mediates cell cycle arrest of ovarian cancer cells.Cell Cycle. 2017 Apr 3;16(7):693-706. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2017.1295181. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Cell Cycle. 2017. PMID: 28278050 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal growth factor modulates claudins and tight junctional functions in ovarian cancer cell lines.Histochem Cell Biol. 2012 Aug;138(2):323-38. doi: 10.1007/s00418-012-0956-x. Epub 2012 Apr 29. Histochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22544349
-
Claudin and ovarian cancer.J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. 2010 Mar 1;11(1):48-54. eCollection 2010. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. 2010. PMID: 24591894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis of ovarian cancer: clues from selected overexpressed genes.Future Oncol. 2009 Dec;5(10):1641-57. doi: 10.2217/fon.09.126. Future Oncol. 2009. PMID: 20001801 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CLDN6-mediates SB431542 action through MMPs to regulate the invasion, migration, and EMT of breast cancer cells.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020 Jul 1;13(7):1590-1600. eCollection 2020. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32782677 Free PMC article.
-
Claudin-9 enhances the metastatic potential of hepatocytes via Tyk2/Stat3 signaling.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2019 Aug;30(8):722-731. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2019.18513. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31418417 Free PMC article.
-
A Role of Tumor-Released Exosomes in Paracrine Dissemination and Metastasis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 10;19(12):3968. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123968. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30544664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging clinical significance of claudin-7 in colorectal cancer: a review.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Sep 20;10:3741-3752. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S175383. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30288105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The claudin family of proteins in human malignancy: a clinical perspective.Cancer Manag Res. 2013 Nov 8;5:367-75. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S38294. Cancer Manag Res. 2013. PMID: 24232410 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Garcia M, Jemal A, Ward EM, Center MM, Hao Y, et al. Global Cancer Facts & Figures 2007. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society; 2007.
-
- Morin PJ. Claudin proteins in human cancer: promising new targets for diagnosis and therapy. Cancer Res. 2005;65:9603–9606. - PubMed
-
- Swisshelm K, Macek R, Kubbies M. Role of claudins in tumorigenesis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005;57:919–928. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

