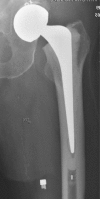
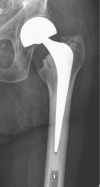
Unipolar versus bipolar Exeter hip hemiarthroplasty: a prospective cohort study on 830 consecutive hips in patients with femoral neck fractures
- PMID: 21789497
- PMCID: PMC3311798
- DOI: 10.1007/s00264-011-1326-3
Unipolar versus bipolar Exeter hip hemiarthroplasty: a prospective cohort study on 830 consecutive hips in patients with femoral neck fractures
Abstract
Background: Hip replacement using a hemiarthroplasty (HA) is a common surgical procedure in elderly patients with fractures of the femoral neck. Data from the Swedish Hip Arthroplasty Register suggest that there is a higher risk for revision surgery with the bipolar HA compared with the unipolar HA.
Purpose: In this study we analysed the reoperation and the dislocation rates for Exeter HAs in patients with a displaced femoral neck fracture, comparing the unipolar and bipolar prosthetic designs. Additionally, we compared the outcome for HAs performed as a primary intervention with those performed secondary to failed internal fixation.
Methods: We studied 830 consecutive Exeter HAs (427 unipolar and 403 bipolar) performed either as a primary operation for a displaced fracture of the femoral neck or as a secondary procedure after failed internal fixation of a fracture of the femoral neck. Cox regression analyses were performed to evaluate factors associated with reoperation and prosthetic dislocation. Age, gender, the surgeon's experience, indication for surgery (primary or secondary) and type of HA (unipolar or bipolar) were tested as independent variables in the model.
Results: The prosthetic design (uni- or bipolar) had no influence on the risk for reoperation or dislocation, nor had the age, gender or the surgeon's experience. The secondary HAs were associated with a significantly increased risk for reoperation (HR 2.6, CI 1.5-4.5) or dislocation (HR 3.3, CI 1.4-7.3) compared to the primary HAs. We found no difference in the risk for reoperation or dislocation when comparing Exeter unipolar and bipolar HAs, but special attention is called for to reduce the risk of prosthesis dislocation and reoperation after a secondary HA.
Figures
References
-
- Calder SJ, Anderson GH, Jagger C, Harper WM, Gregg PJ. Unipolar or bipolar prosthesis for displaced intracapsular hip fracture in octogenarians: a randomised prospective study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996;78:391–394. - PubMed
-
- Cornell CN, Levine D, O'Doherty J, Lyden J (1998) Unipolar versus bipolar hemiarthroplasty for the treatment of femoral neck fractures in the elderly. Clin Orthop Relat Res 348:67–71 - PubMed
-
- Raia FJ, Chapman CB, Herrera MF, Schweppe MW, Michelsen CB, Rosenwasser MP (2003) Unipolar or bipolar hemiarthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in the elderly? Clin Orthop Relat Res 414:259–265 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical