Structural basis of the antiproliferative activity of largazole, a depsipeptide inhibitor of the histone deacetylases
- PMID: 21790156
- PMCID: PMC3162211
- DOI: 10.1021/ja205972n
Structural basis of the antiproliferative activity of largazole, a depsipeptide inhibitor of the histone deacetylases
Abstract
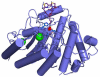
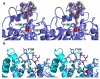
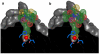
Largazole is a macrocyclic depsipeptide originally isolated from the marine cyanobacterium Symploca sp., which is indigenous to the warm, blue-green waters of Key Largo, Florida (whence largazole derives its name). Largazole contains an unusual thiazoline-thiazole ring system that rigidifies its macrocyclic skeleton, and it also contains a lipophilic thioester side chain. Hydrolysis of the thioester in vivo yields largazole thiol, which exhibits remarkable antiproliferative effects and is believed to be the most potent inhibitor of the metal-dependent histone deacetylases (HDACs). Here, the 2.14 Å-resolution crystal structure of the HDAC8-largazole thiol complex is the first of an HDAC complexed with a macrocyclic inhibitor and reveals that ideal thiolate-zinc coordination geometry is the key chemical feature responsible for its exceptional affinity and biological activity. Notably, the core structure of largazole is conserved in romidepsin, a depsipeptide natural product formulated as the drug Istodax recently approved for cancer chemotherapy. Accordingly, the structure of the HDAC8-largazole thiol complex is the first to illustrate the mode of action of a new class of therapeutically important HDAC inhibitors.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

