Innate immune control of West Nile virus infection
- PMID: 21790942
- PMCID: PMC3196381
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2011.01649.x
Innate immune control of West Nile virus infection
Abstract
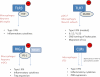
West Nile virus (WNV), from the Flaviviridae family, is a re-emerging zoonotic pathogen of medical importance. In humans, WNV infection may cause life-threatening meningoencephalitis or long-term neurologic sequelae. WNV is transmitted by Culex spp. mosquitoes and both the arthropod vector and the mammalian host are equipped with antiviral innate immune mechanisms sharing a common phylogeny. As far as the current evidence is able to demonstrate, mosquitoes primarily rely on RNA interference, Toll, Imd and JAK-STAT signalling pathways for limiting viral infection, while mammals are provided with these and other more complex antiviral mechanisms involving antiviral effectors, inflammatory mediators, and cellular responses triggered by highly specialized pathogen detection mechanisms that often resemble their invertebrate ancestry. This mini-review summarizes our current understanding of how the innate immune systems of the vector and the mammalian host react to WNV infection and shape its pathogenesis.
© 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
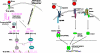
References
-
- Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R, Flavell RA. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature. 2001;413:732–738. - PubMed
-
- Aravin AA, Hannon GJ, Brennecke J. The Piwi-piRNA pathway provides an adaptive defense in the transposon arms race. Science (New York, N.Y. 2007;318:761–764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U54-AI057158/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI070343/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- AI-50031/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI041440/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI032947/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI050031/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 AI057158/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI-055749/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI089992/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI079360/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- N01 AI500031/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI055749/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

