High central venous oxygen saturation in the latter stages of septic shock is associated with increased mortality
- PMID: 21791065
- PMCID: PMC3387619
- DOI: 10.1186/cc10325
High central venous oxygen saturation in the latter stages of septic shock is associated with increased mortality
Abstract
Introduction: Current guidelines recommend maintaining central venous oxygen saturation (ScvO2) higher than 70% in patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. As high levels of ScvO2 may reflect an inadequate use of oxygen, our aim was to evaluate the relation between maximal ScvO2 levels (ScvO2max) and survival among intensive care unit (ICU) patients with septic shock.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed data from all admissions to our ICU between January 2008 and December 2009. All septic shock patients in whom the ScvO2 was measured were included. The measures of ScvO2max within the first 72 hours after the onset of shock were collected.
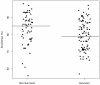
Results: A total of 1,976 patients were screened and 152 (7.7%) patients met the inclusion criteria. The level of ScvO2max was 85% (78 to 89) in the non-survivors, compared with 79% (72 to 87) in the survivors (P = 0.009).
Conclusions: Our findings raise concerns about high levels of ScvO2 in patients with septic shock. This may reflect the severity of the shock with an impaired oxygen use. Future strategies may target an optimization of tissue perfusion in this specific subgroup of patients.
Figures
Comment in
-
Central venous oxygen saturation in septic shock--a marker of cardiac output, microvascular shunting and/or dysoxia?Crit Care. 2011 Aug 18;15(4):184. doi: 10.1186/cc10314. Crit Care. 2011. PMID: 21892975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J, Parker MM, Jaeschke R, Reinhart K, Angus DC, Brun-Buisson C, Beale R, Calandra T, Dhainaut J, Gerlach H, Harvey M, Marini JJ, Marshall J, Ranieri M, Ramsay G, Sevransky J, Thompson BT, Townsend S, Vender JS, Zimmerman JL, Vincent J. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:296–327. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000298158.12101.41. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, De Mendonça A, Bruining H, Reinhart CK, Suter PM, Thijs LG. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med. 1996;22:707–710. doi: 10.1007/BF01709751. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous