Global and organ-specific chronic graft-versus-host disease severity according to the 2005 NIH Consensus Criteria
- PMID: 21791424
- PMCID: PMC3204740
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2011-03-344390
Global and organ-specific chronic graft-versus-host disease severity according to the 2005 NIH Consensus Criteria
Abstract
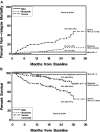
In 2005, the National Institutes of Health Consensus Development Project on Criteria for Clinical Trials in Chronic GVHD proposed a new scoring system for individual organs and an algorithm for calculating global severity (mild, moderate, severe). The Chronic GVHD Consortium was established to test these new criteria. This report includes the first 298 adult patients enrolled at 5 centers of the Consortium. Patients were assessed every 3-6 months using standardized forms recommended by the Consensus Conference. At the time of study enrollment, global chronic GVHD severity was mild in 10% (n = 32), moderate in 59% (n = 175), and severe in 31% (n = 91). Skin, lung, or eye scores determined the global severity score in the majority of cases, with the other 5 organs determining 16% of the global severity scores. Conventional risk factors predictive for onset of chronic GVHD and nonrelapse mortality in people with chronic GVHD were not associated with NIH global severity scores. Global severity scores at enrollment were associated with nonrelapse mortality (P < .0001) and survival (P < .0001); 2-year overall survival was 62% (severe), 86% (moderate), and 97% (mild). Patients with mild chronic GVHD have a good prognosis, while patients with severe chronic GVHD have a poor prognosis. This study was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as no. NCT00637689.
Figures
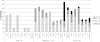
References
-
- Lee SJ, Klein JP, Barrett AJ, et al. Severity of chronic graft-versus-host disease: association with treatment-related mortality and relapse. Blood. 2002;100(2):406–414. - PubMed
-
- Shulman HM, Sullivan KM, Weiden PL, et al. Chronic graft-versus-host syndrome in man. A long-term clinicopathologic study of 20 Seattle patients. Am J Med. 1980;69(2):204–217. - PubMed
-
- Filipovich AH, Weisdorf D, Pavletic S, et al. National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: I. Diagnosis and staging working group report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2005;11(12):945–956. - PubMed
-
- Schultz KR, Miklos DB, Fowler D, et al. Toward biomarkers for chronic graft-versus-host disease: National Institutes of Health consensus development project on criteria for clinical trials in chronic graft-versus-host disease: III. Biomarker Working Group Report. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2006;12(2):126–137. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

