Rhinacanthus nasutus protects cultured neuronal cells against hypoxia induced cell death
- PMID: 21792150
- PMCID: PMC6264774
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules16086322
Rhinacanthus nasutus protects cultured neuronal cells against hypoxia induced cell death
Abstract
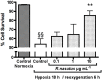
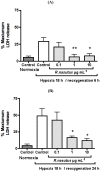
Rhinacanthus nasutus (L.) Kurz (Acanthaceae) is an herb native to Thailand and Southeast Asia, known for its antioxidant properties. Hypoxia leads to an increase in reactive oxygen species in cells and is a leading cause of neuronal damage. Cell death caused by hypoxia has been linked with a number of neurodegenerative diseases including some forms of dementia and stroke, as well as the build up of reactive oxygen species which can lead to diseases such as Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease and Alzeheimer's disease. In this study we used an airtight culture container and the Mitsubishi Gas Company anaeropack along with the MTT assay, LDH assay and the trypan blue exlusion assay to show that 1 and 10 µg mL⁻¹ root extract of R. nasutus is able to significantly prevent the death of HT-22 cells subjected to hypoxic conditions, and 0.1 to 10 µg mL⁻¹ had no toxic effect on HT-22 under normal conditions, whereas 100 µg mL⁻¹ reduced HT-22 cell proliferation. We also used H₂DCFDA staining to show R. nasutus can reduce reactive oxygen species production in HT-22 cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Shimada S., Hirabayashi M., Ishige K., Kosuge Y., Kihara T., Ito Y. Activation of dopamine D4 receptors is protective against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cell death in HT22 cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010;114:217–224. - PubMed
-
- Hartman P., Ponder R., Lo H.H., Ishii N. Mitochondrial oxidative stress can lead to nuclear hypermutability. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2004;125:417–420. - PubMed
-
- Jefferson J.A., Simoni J., Escudero E., Hurtado M.E., Swenson E.R., Wesson D.E., Schreiner G.F., Schoene R.B., Johnson R.J., Hurtado A. Increased oxidative stress following acute and chronic high altitude exposure. High Alt. Med. Biol. 2004;5:61–69. - PubMed
-
- Jin D.Q., Lim C.S., Hwang J.K., Ha I., Han J.S. Anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of macelignan in murine hippocampal cell line and primary culture of rat microglial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005;331:1264–1269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

