Ophthalmoplegia associated with transorbital penetrating brainstem injury by broken fishing pole
- PMID: 21792279
- PMCID: PMC3141853
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S22821
Ophthalmoplegia associated with transorbital penetrating brainstem injury by broken fishing pole
Abstract
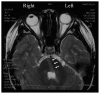
We report our findings in a case of ophthalmoplegia caused by a transorbital penetrating brainstem injury. An 8-year-old boy was accidentally injured by a broken fishing fiberglass pole which penetrated through the right orbit and entered the brainstem. Magnetic resonance imaging showed a linear wound that entered and passed through the pons obliquely and reached the fourth cerebral ventricle and cerebellar vermis. He had a left-sided hemiplegia and left facial nerve palsy and was diagnosed with "one-and-a-half syndrome". His hemiplegia and left facial nerve palsy resolved in 2 weeks leaving only a left abducens nerve palsy. The eye position and eye movements fully recovered within 3 months. These findings suggest a good prognosis for this type of trauma unless life-threatening changes develop.
Keywords: penetrating orbitocranial injury; penetrating orbitocranial trauma; trauma.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transorbital orbitocranial penetrating injury caused by a metal bar.J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2012 May;3(2):178-81. doi: 10.4103/0976-3147.98228. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2012. PMID: 22865972 Free PMC article.
-
[Bilateral traumatic abducens nerve palsy without skull fracture or intracranial hematoma-a report of 3 cases and consideration of the mechanism of injury (author's transl)].No Shinkei Geka. 1976 Oct;4(10):963-9. No Shinkei Geka. 1976. PMID: 1033472 Japanese.
-
[Case of pontine infarction causing alternating hemiplegia with ipsilateral abducens nerve palsy and contralateral supranuclear facial nerve palsy].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2008 Feb;48(2):135-8. doi: 10.5692/clinicalneurol.48.135. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2008. PMID: 18326308 Japanese.
-
Orbitocranial Low-Velocity Penetrating Injury: A Personal Experience, Case Series, Review of the literature, and Proposed Management Plan.World Neurosurg. 2016 Mar;87:26-34. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2015.12.063. Epub 2015 Dec 24. World Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26724632 Review.
-
The Role of Intraoperative Cerebral Angiography in Transorbital Intracranial Penetrating Trauma: A Case Report and Literature Review.World Neurosurg. 2017 Jan;97:761.e5-761.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2016.09.083. Epub 2016 Sep 28. World Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 27693768 Review.
References
-
- Bard LA, Jarrett WH. Intracranial complications of penetrating orbital injuries. Arch Ophthalmol. 1964;71:332–343. - PubMed
-
- Miller CF, Brodkey JS, Colombi BJ. The danger of intracranial wood. Surg Neurol. 1977;7:95–103. - PubMed
-
- Doucet TW, Harper DW, Rogers J. Penetrating orbital foreign body with intracranial involvement. Ann Ophthalmol. 1983;15:325–327. - PubMed
-
- Michon JJ, Miller NR. Management of combined penetrating intraorbital and intracranial trauma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1993;111:438–439. - PubMed
-
- Smely C, Orszagh M. Intracranial transorbital injury by a wooden foreign body: re-evaluation of CT and MRI findings. Br J Neurosurg. 1999;13:206–211. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

