Update on optimal use of omalizumab in management of asthma
- PMID: 21792319
- PMCID: PMC3140296
- DOI: 10.2147/JAA.S14520
Update on optimal use of omalizumab in management of asthma
Abstract
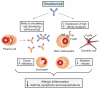
Omalizumab is a humanized monoclonal anti-IgE antibody recently approved for the treatment of severe allergic asthma. This drug inhibits allergic responses by binding to serum IgE, thus preventing interaction with cellular IgE receptors. Omalizumab is also capable of downregulating the expression of high affinity IgE receptors on inflammatory cells, as well as the numbers of eosinophils in both blood and induced sputum. The clinical effects of omalizumab include improvements in respiratory symptoms and quality of life, paralleled by a reduction of asthma exacerbations, emergency room visits, and use of systemic corticosteroids and rescue bronchodilators. Omalizumab is relatively well-tolerated, and only rarely induces anaphylactic reactions. Therefore, this drug represents a valid option as add-on therapy for patients with severe persistent allergic asthma inadequately controlled by high doses of standard inhaled treatments.
Keywords: anti-IgE; omalizumab; severe asthma.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson GP. Endotyping asthma: new insights into key pathogenetic mechanisms in a complex, heterogeneous disease. Lancet. 2008;372(9643):1107–1119. - PubMed
-
- Anandan C, Nurmatov U, van Schayck OCP, Skeih A. Is the prevalence of asthma declining? Systematic review of epidemiological studies. Allergy. 2010;65(2):152–167. - PubMed
-
- Masoli M, Fabian D, Holt S, Beasley R. The global burden of asthma: executive summary of the GINA dissemination committee report. Allergy. 2004;59(5):469–478. - PubMed
-
- Bateman ED, Boushey HA, Bousquet J, et al. Can guideline-defined asthma control be achieved? The Gaining Optimal Asthma ControL (GOAL) study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004;170(8):836–844. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

