How ongoing neuronal oscillations account for evoked fMRI variability
- PMID: 21795550
- PMCID: PMC6623098
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0210-11.2011
How ongoing neuronal oscillations account for evoked fMRI variability
Abstract
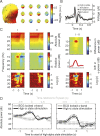
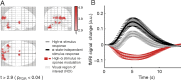
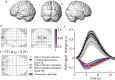
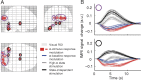
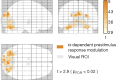
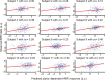
Variability of evoked single-trial responses despite constant input or task is a feature of large-scale brain signals recorded by fMRI. Initial evidence signified relevance of fMRI signal variability for perception and behavior. Yet the underlying intrinsic neuronal sources have not been previously substantiated. Here, we address this issue using simultaneous EEG-fMRI and real-time classification of ongoing alpha-rhythm states triggering visual stimulation in human subjects. We investigated whether spontaneous neuronal oscillations-as reflected in the posterior alpha rhythm-account for variability of evoked fMRI responses. Based on previous work, we specifically hypothesized linear superposition of fMRI activity related to fluctuations of ongoing alpha rhythm and a visually evoked fMRI response. We observed that spontaneous alpha-rhythm power fluctuations largely explain evoked fMRI response variance in extrastriate, thalamic, and cerebellar areas. For extrastriate areas, we confirmed the linear superposition hypothesis. We hence linked evoked fMRI response variability to an intrinsic rhythm's power fluctuations. These findings contribute to our conceptual understanding of how brain rhythms can account for trial-by-trial variability in stimulus processing.
Figures



References
-
- Anami K, Mori T, Tanaka F, Kawagoe Y, Okamoto J, Yarita M, Ohnishi T, Yumoto M, Matsuda H, Saitoh O. Stepping stone sampling for retrieving artifact-free electroencephalogram during functional magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage. 2003;19:281–295. - PubMed
-
- Arieli A, Sterkin A, Grinvald A, Aertsen A. Dynamics of ongoing activity: explanation of the large variability in evoked cortical responses. Science. 1996;273:1868–1871. - PubMed
-
- Babiloni C, Brancucci A, Del Percio C, Capotosto P, Arendt-Nielsen L, Chen AC, Rossini PM. Anticipatory electroencephalography alpha rhythm predicts subjective perception of pain intensity. J Pain. 2006;7:709–717. - PubMed
-
- Becker R, Ritter P, Villringer A. Influence of ongoing alpha rhythm on the visual evoked potential. Neuroimage. 2008;39:707–716. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
