Oxytocin reduces background anxiety in a fear-potentiated startle paradigm: peripheral vs central administration
- PMID: 21796104
- PMCID: PMC3194076
- DOI: 10.1038/npp.2011.138
Oxytocin reduces background anxiety in a fear-potentiated startle paradigm: peripheral vs central administration
Abstract
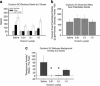
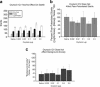
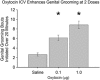
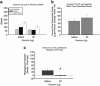
Oxytocin is known to have anti-anxiety and anti-stress effects. Using a fear-potentiated startle paradigm in rats, we previously demonstrated that subcutaneously administered oxytocin suppressed acoustic startle following fear conditioning compared with startle before fear conditioning (termed background anxiety), but did not have an effect on cue-specific fear-potentiated startle. The findings suggest oxytocin reduces background anxiety, an anxious state not directly related to cue-specific fear, but sustained beyond the immediate threat. The goal of the present study was to compare the effects of centrally and peripherally administered oxytocin on background anxiety and cue-specific fear. Male rats were given oxytocin either subcutaneously (SC) or intracerebroventricularly (ICV) into the lateral ventricles before fear-potentiated startle testing. Oxytocin doses of 0.01 and 0.1 μg/kg SC reduced background anxiety. ICV administration of oxytocin at doses from 0.002 to 20 μg oxytocin had no effect on background anxiety or cue-specific fear-potentiated startle. The 20 μg ICV dose of oxytocin did reduce acoustic startle in non-fear conditioned rats. These studies indicate that oxytocin is potent and effective in reducing background anxiety when delivered peripherally, but not when delivered into the cerebroventricular system. Oxytocin given systemically may have anti-anxiety properties that are particularly germane to the hypervigilance and exaggerated startle typically seen in many anxiety and mental health disorder patients.
Figures

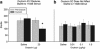
References
-
- Amico JA, Vollmer RR, Karam JR, Lee PR, Li X, Koenig JI, et al. Centrally administered oxytocin elicits exaggerated grooming in oxytocin null mice. Pharmacol, Biochem, Behav. 2004;78:333–339. - PubMed
-
- Bartz J, Hollander E. Oxytocin and experimental therapeutics in autism spectrum disorders. Prog Brain Res. 2008;170:451–462. - PubMed
-
- Bernier R, Dawson G, Panagiotides H, Webb S. Individuals with autism spectrum disorder show normal responses to a fear potential startle paradigm. J Autism Dev Disord. 2005;35:575–583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

