Inhibition of sonic hedgehog pathway and pluripotency maintaining factors regulate human pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics
- PMID: 21796625
- PMCID: PMC3480310
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.26323
Inhibition of sonic hedgehog pathway and pluripotency maintaining factors regulate human pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics
Abstract
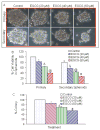
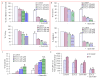
Activation of the sonic hedgehog (SHh) pathway is required for the growth of numerous tissues and organs and recent evidence indicates that this pathway is often recruited to stimulate growth of cancer stem cells (CSCs) and to orchestrate the reprogramming of cancer cells via epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT). The objectives of this study were to examine the molecular mechanisms by which (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG), an active compound in green tea, inhibits self-renewal capacity of pancreatic CSCs and synergizes with quercetin, a major polyphenol and flavonoid commonly detected in many fruits and vegetables. Our data demonstrated that EGCG inhibited the expression of pluripotency maintaining transcription factors (Nanog, c-Myc and Oct-4) and self-renewal capacity of pancreatic CSCs. Inhibition of Nanog by shRNA enhanced the inhibitory effects of EGCG on self-renewal capacity of CSCs. EGCG inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis by inhibiting the expression of Bcl-2 and XIAP and activating caspase-3. Interestingly, EGCG also inhibited the components of SHh pathway (smoothened, patched, Gli1 and Gli2) and Gli transcriptional activity. Furthermore, EGCG inhibited EMT by inhibiting the expression of Snail, Slug and ZEB1, and TCF/LEF transcriptional activity, which correlated with significantly reduced CSC's migration and invasion, suggesting the blockade of signaling involved in early metastasis. Furthermore, combination of quercetin with EGCG had synergistic inhibitory effects on self-renewal capacity of CSCs through attenuation of TCF/LEF and Gli activities. Since aberrant SHh signaling occurs in pancreatic tumorigenesis, therapeutics that target SHh pathway may improve the outcomes of patients with pancreatic cancer by targeting CSCs.
Copyright © 2011 UICC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Sanguinarine inhibits pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics by inducing oxidative stress and suppressing sonic hedgehog-Gli-Nanog pathway.Carcinogenesis. 2017 Oct 1;38(10):1047-1056. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgx070. Carcinogenesis. 2017. PMID: 28968696
-
Sulforaphane regulates self-renewal of pancreatic cancer stem cells through the modulation of Sonic hedgehog-GLI pathway.Mol Cell Biochem. 2013 Jan;373(1-2):217-27. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1493-6. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Mol Cell Biochem. 2013. PMID: 23129257
-
Inhibition of pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics by α-Mangostin: Molecular mechanisms involving Sonic hedgehog and Nanog.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Apr;23(4):2719-2730. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14178. Epub 2019 Feb 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 30712329 Free PMC article.
-
Human cancer stem cells are a target for cancer prevention using (-)-epigallocatechin gallate.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017 Dec;143(12):2401-2412. doi: 10.1007/s00432-017-2515-2. Epub 2017 Sep 23. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28942499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Cancer Stem Cells for Chemoprevention of Pancreatic Cancer.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(22):2585-2594. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170127095832. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28137215 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro and in vivo antitumoral effects of combinations of polyphenols, or polyphenols and anticancer drugs: perspectives on cancer treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Apr 24;16(5):9236-82. doi: 10.3390/ijms16059236. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25918934 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting lung cancer stem-like cells with TRAIL gene armed oncolytic adenovirus.J Cell Mol Med. 2015 May;19(5):915-23. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12397. Epub 2015 Feb 16. J Cell Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25683371 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol exposure of human pancreatic normal ductal epithelial cells induces EMT phenotype and enhances pancreatic cancer development in KC (Pdx1-Cre and LSL-KrasG12D ) mice.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Jan;26(2):399-409. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17092. Epub 2021 Dec 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 34859959 Free PMC article.
-
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits nasopharyngeal cancer stem cell self-renewal and migration and reverses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via NF-κB p65 inactivation.Tumour Biol. 2015 Apr;36(4):2747-61. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2899-4. Epub 2014 Dec 7. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25487615
-
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate targets cancer stem-like cells and enhances 5-fluorouracil chemosensitivity in colorectal cancer.Oncotarget. 2016 Mar 29;7(13):16158-71. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.7567. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26930714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:277–300. - PubMed
-
- Pliarchopoulou K, Pectasides D. Pancreatic cancer: current and future treatment strategies. Cancer Treat Rev. 2009;35:431–6. - PubMed
-
- Magee CJ, Ghaneh P, Neoptolemos JP. Surgical and medical therapy for pancreatic carcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2002;16:435–55. - PubMed
-
- Yeo TP, Hruban RH, Leach SD, Wilentz RE, Sohn TA, Kern SE, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Maitra A, Goggins M, Canto MI, Abrams RA, Laheru D, et al. Pancreatic cancer. Curr Probl Cancer. 2002;26:176–275. - PubMed
-
- Warshaw AL, Fernandez-del Castillo C. Pancreatic carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1992;326:455–65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

