Bupropion-SR for smoking cessation in early recovery from alcohol dependence: a placebo-controlled, double-blind pilot study
- PMID: 21797811
- PMCID: PMC4048722
- DOI: 10.3109/00952990.2011.598591
Bupropion-SR for smoking cessation in early recovery from alcohol dependence: a placebo-controlled, double-blind pilot study
Abstract
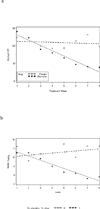
We conducted a double-blind pilot study involving 11 alcohol- and nicotine-dependent patients randomized to receive either bupropion or placebo. Four of six patients on bupropion and one of five patients on placebo were abstinent from smoking at the end of medication phase. Those in the bupropion group reported significantly less craving (p < .02) and less exposure to cigarette smoke over time (expired carbon monoxide; p < .01). There were no serious adverse events and no main effects of medication group on either per subject or total number of adverse events. All those who completed treatment remained abstinent from alcohol.
Figures
References
-
- CDC. Cigarette use among high school students--United States, 1991–2009. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2010;59(26):797–801. - PubMed
-
- Bobo JK. Nicotine dependence and alcoholism epidemiology and treatment. J Psychoactive Drugs. 1989 Jul;21(3):323–329. - PubMed
-
- Joseph AM. Nicotine treatment at the Drug Dependency Program of the Minneapolis VA Medical Center. A researcher's perspective. J Subst Abuse Treat. 1993 Mar;10(2):147–152. - PubMed
-
- Hurt RD, Offord KP, Croghan IT, et al. Mortality following inpatient addictions treatment. Role of tobacco use in a community-based cohort. JAMA. 1996 Apr 10;275(14):1097–1103. - PubMed
-
- Hays JT, Schroeder DR, Offord KP, et al. Response to nicotine dependence treatment in smokers with current and past alcohol problems. Ann Behav Med. 1999;21(3):244–250. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials