Deletion of neuronal gap junction protein connexin 36 impairs hippocampal LTP
- PMID: 21798314
- PMCID: PMC3159746
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2011.07.018
Deletion of neuronal gap junction protein connexin 36 impairs hippocampal LTP
Abstract
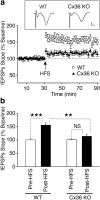
In the mammalian CNS, deletion of neuronal gap junction protein, connexin 36 (Cx36), causes deficiencies in learning and memory. Here we tested whether Cx36 deletion affects the hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP), which is considered as a cellular model of learning and memory mechanisms. We report that in acute slices of the hippocampal CA1 area, LTP is reduced in Cx36 knockout mice as compared to wild-type mice. Western blot analysis of NMDA receptor subunits indicates a higher NR2A/NR2B ratio in Cx36 knockout mice, indicating that there is shift in the threshold for LTP induction in knockout animals. Data suggest a possibility that learning and memory deficiencies in Cx36 knockout mice are due to deficiencies in LTP mechanisms.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NR2A-containing NMDA receptors are required for L-LTP induction and depotentiation in CA1 region of hippocampal slices.Eur J Neurosci. 2009 Jun;29(11):2137-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06783.x. Epub 2009 May 21. Eur J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19490087
-
Therapeutic significance of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors and mGluR5 metabotropic glutamate receptors in mediating the synaptotoxic effects of β-amyloid oligomers on long-term potentiation (LTP) in murine hippocampal slices.Neuropharmacology. 2011 May;60(6):982-90. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.01.051. Epub 2011 Feb 12. Neuropharmacology. 2011. PMID: 21310164
-
Induction- and conditioning-protocol dependent involvement of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in synaptic potentiation and contextual fear memory in the hippocampal CA1 region of rats.Mol Brain. 2008 Sep 30;1:9. doi: 10.1186/1756-6606-1-9. Mol Brain. 2008. PMID: 18826591 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal long-term synaptic plasticity and signal amplification of NMDA receptors.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006;18(1-2):71-84. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v18.i1-2.80. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 2006. PMID: 17725510 Review.
-
NMDA receptor-dependent long-term potentiation comprises a family of temporally overlapping forms of synaptic plasticity that are induced by different patterns of stimulation.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013 Dec 2;369(1633):20130131. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0131. Print 2014 Jan 5. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2013. PMID: 24298134 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of gap junction channels by infectious agents and inflammation in the CNS.Front Cell Neurosci. 2014 May 9;8:122. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00122. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24847208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connexins and pannexins: At the junction of neuro-glial homeostasis & disease.J Neurosci Res. 2018 Jan;96(1):31-44. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24088. Epub 2017 Jun 5. J Neurosci Res. 2018. PMID: 28580666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gap Junctional Blockade Stochastically Induces Different Species-Specific Head Anatomies in Genetically Wild-Type Girardia dorotocephala Flatworms.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Nov 24;16(11):27865-96. doi: 10.3390/ijms161126065. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26610482 Free PMC article.
-
Gap junctional signaling in pattern regulation: Physiological network connectivity instructs growth and form.Dev Neurobiol. 2017 May;77(5):643-673. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22405. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Dev Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27265625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuronal gap junctions: making and breaking connections during development and injury.Trends Neurosci. 2013 Apr;36(4):227-36. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2012.11.001. Epub 2012 Dec 11. Trends Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23237660 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bao X, Pal R, Hascup KN, Wang Y, Wang WT, Xu W, Hui D, Agbas A, Wang X, Michaelis ML, Choi IY, Belousov AB, Gerhardt GA, Michaelis EK. Transgenic expression of Glud1 (glutamate dehydrogenase 1) in neurons: in vivo model of enhanced glutamate release, altered synaptic plasticity, and selective neuronal vulnerability. J Neurosci. 2009;29:13929–13944. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belluardo N, Mudo G, Trovato-Salinaro A, Le Gurun S, Charollais A, Serre-Beinier V, Amato G, Haefliger JA, Meda P, Condorelli DF. Expression of connexin36 in the adult and developing rat brain. Brain Res. 2000;865:121–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

