Deletion of neuronal gap junction protein connexin 36 impairs hippocampal LTP
- PMID: 21798314
- PMCID: PMC3159746
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2011.07.018
Deletion of neuronal gap junction protein connexin 36 impairs hippocampal LTP
Abstract
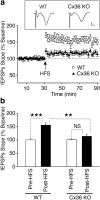
In the mammalian CNS, deletion of neuronal gap junction protein, connexin 36 (Cx36), causes deficiencies in learning and memory. Here we tested whether Cx36 deletion affects the hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP), which is considered as a cellular model of learning and memory mechanisms. We report that in acute slices of the hippocampal CA1 area, LTP is reduced in Cx36 knockout mice as compared to wild-type mice. Western blot analysis of NMDA receptor subunits indicates a higher NR2A/NR2B ratio in Cx36 knockout mice, indicating that there is shift in the threshold for LTP induction in knockout animals. Data suggest a possibility that learning and memory deficiencies in Cx36 knockout mice are due to deficiencies in LTP mechanisms.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Bao X, Pal R, Hascup KN, Wang Y, Wang WT, Xu W, Hui D, Agbas A, Wang X, Michaelis ML, Choi IY, Belousov AB, Gerhardt GA, Michaelis EK. Transgenic expression of Glud1 (glutamate dehydrogenase 1) in neurons: in vivo model of enhanced glutamate release, altered synaptic plasticity, and selective neuronal vulnerability. J Neurosci. 2009;29:13929–13944. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belluardo N, Mudo G, Trovato-Salinaro A, Le Gurun S, Charollais A, Serre-Beinier V, Amato G, Haefliger JA, Meda P, Condorelli DF. Expression of connexin36 in the adult and developing rat brain. Brain Res. 2000;865:121–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

