Increased growth rate of vestibular schwannoma after resection of contralateral tumor in neurofibromatosis type 2
- PMID: 21798887
- PMCID: PMC3177662
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nor101
Increased growth rate of vestibular schwannoma after resection of contralateral tumor in neurofibromatosis type 2
Abstract
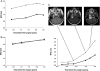
Surgical management of bilateral vestibular schwannomas (VS) in neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2) is often difficult, especially when both tumors threaten the brainstem. When the largest tumor has been removed, the management of the contralateral VS may become puzzling. To give new insights into the growth pattern of these tumors and to determine the best time point for treatment (surgery or medical treatment), we studied radiological growth in 11 VS (11 patients with NF2) over a long period (mean duration, 7.6 years), before and after removal of the contralateral tumor while both were threatening the brainstem. We used a quantitative approach of the radiological velocity of diametric expansion (VDE) on consecutive magnetic resonance images. Before first surgery, growth patterns of both tumors were similar in 9 of 11 cases. After the first surgery, VDE of the remaining VS was significantly elevated, compared with the preoperative period (2.5 ± 2.2 vs 4.4 ± 3.4 mm/year; P = .01, by Wilcoxon test). Decrease in hearing function was associated with increased postoperative growth in 3 cases. Growth pattern of coexisting intracranial meningiomas was not modified by VS surgery on the first side. In conclusion, removal of a large VS in a patient with NF2 might induce an increase in the growth rate of the contralateral medium or large VS. This possibility should be integrated in NF2 patient management to adequately treat the second VS.
Figures

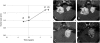
References
-
- Evans DG, Moran A, King A, Saeed S, Gurusinghe N, Ramsden R. Incidence of vestibular schwannoma and neurofibromatosis 2 in the North West of England over a 10-year period: higher incidence than previously thought. Otol Neurotol. 2005;26(1):93–97. doi:10.1097/00129492-200501000-00016. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brackmann DE, Fayad JN, Slattery WH, 3rd, et al. Early proactive management of vestibular schwannomas in neurofibromatosis type 2. Neurosurgery. 2001;49(2):274–280. discussion 280–273. - PubMed
-
- Samii M, Matthies C, Tatagiba M. Management of vestibular schwannomas (acoustic neuromas): auditory and facial nerve function after resection of 120 vestibular schwannomas in patients with neurofibromatosis 2. Neurosurgery. 1997;40(4):696–705. discussion 705–696 doi:10.1097/00006123-199704000-00007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Lunsford LD. Results of acoustic neuroma radiosurgery: an analysis of 5 years' experience using current methods. J Neurosurg. 2001;94(1):1–6. - PubMed
-
- Evans DG, Kalamarides M, Hunter-Schaedle K, et al. Consensus recommendations to accelerate clinical trials for neurofibromatosis type 2. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(16):5032–5039. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-3011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

