Src homology domain 2-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase-1 (SHP-1) binds and dephosphorylates G(alpha)-interacting, vesicle-associated protein (GIV)/Girdin and attenuates the GIV-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt signaling pathway
- PMID: 21799016
- PMCID: PMC3173146
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.275685
Src homology domain 2-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase-1 (SHP-1) binds and dephosphorylates G(alpha)-interacting, vesicle-associated protein (GIV)/Girdin and attenuates the GIV-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt signaling pathway
Abstract
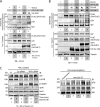
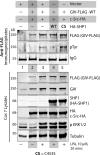
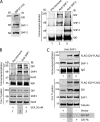
GIV (Gα-interacting vesicle-associated protein, also known as Girdin) is a bona fide enhancer of PI3K-Akt signals during a diverse set of biological processes, e.g. wound healing, macrophage chemotaxis, tumor angiogenesis, and cancer invasion/metastasis. We recently demonstrated that tyrosine phosphorylation of GIV by receptor and non-receptor-tyrosine kinases is a key step that is required for GIV to directly bind and enhance PI3K activity. Here we report the discovery that Src homology 2-containing phosphatase-1 (SHP-1) is the major protein-tyrosine phosphatase that targets two critical phosphotyrosines within GIV and antagonizes phospho-GIV-dependent PI3K enhancement in mammalian cells. Using phosphorylation-dephosphorylation assays, we demonstrate that SHP-1 is the major and specific protein-tyrosine phosphatase that catalyzes the dephosphorylation of tyrosine-phosphorylated GIV in vitro and inhibits ligand-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of GIV downstream of both growth factor receptors and GPCRs in cells. In vitro binding and co-immunoprecipitation assays demonstrate that SHP-1 and GIV interact directly and constitutively and that this interaction occurs between the SH2 domain of SHP-1 and the C terminus of GIV. Overexpression of SHP-1 inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation of GIV and formation of phospho-GIV-PI3K complexes, and specifically suppresses GIV-dependent activation of Akt. Consistently, depletion of SHP-1 enhances peak tyrosine phosphorylation of GIV, which coincides with an increase in peak Akt activity. We conclude that SHP-1 antagonizes the action of receptor and non-receptor-tyrosine kinases on GIV and down-regulates the phospho-GIV-PI3K-Akt axis of signaling.
Figures
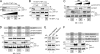



References
-
- Enomoto A., Murakami H., Asai N., Morone N., Watanabe T., Kawai K., Murakumo Y., Usukura J., Kaibuchi K., Takahashi M. (2005) Dev. Cell 9, 389–402 - PubMed
-
- Jiang P., Enomoto A., Jijiwa M., Kato T., Hasegawa T., Ishida M., Sato T., Asai N., Murakumo Y., Takahashi M. (2008) Cancer Res. 68, 1310–1318 - PubMed
-
- Kitamura T., Asai N., Enomoto A., Maeda K., Kato T., Ishida M., Jiang P., Watanabe T., Usukura J., Kondo T., Costantini F., Murohara T., Takahashi M. (2008) Nat. Cell Biol. 10, 329–337 - PubMed
-
- Anai M., Shojima N., Katagiri H., Ogihara T., Sakoda H., Onishi Y., Ono H., Fujishiro M., Fukushima Y., Horike N., Viana A., Kikuchi M., Noguchi N., Takahashi S., Takata K., Oka Y., Uchijima Y., Kurihara H., Asano T. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280, 18525–18535 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

