Hepatocyte spheroid arrays inside microwells connected with microchannels
- PMID: 21799712
- PMCID: PMC3145231
- DOI: 10.1063/1.3576905
Hepatocyte spheroid arrays inside microwells connected with microchannels
Abstract
Spheroid culture is a preferable cell culture approach for some cell types, including hepatocytes, as this type of culture often allows maintenance of organ-specific functions. In this study, we describe a spheroid microarray chip (SM chip) that allows stable immobilization of hepatocyte spheroids in microwells and that can be used to evaluate drug metabolism with high efficiency. The SM chip consists of 300-μm-diameter cylindrical wells with chemically modified bottom faces that form a 100-μm-diameter cell adhesion region surrounded by a nonadhesion region. Primary hepatocytes seeded onto this chip spontaneously formed spheroids of uniform diameter on the cell adhesion region in each microwell and these could be used for cytochrome P-450 fluorescence assays. A row of microwells could also be connected to a microchannel for simultaneous detection of different cytochrome P-450 enzyme activities on a single chip. The miniaturized features of this SM chip reduce the numbers of cells and the amounts of reagents required for assays. The detection of four cytochrome P-450 enzyme activities was demonstrated following induction by 3-methylcholantlene, with a sensitivity significantly higher than that in conventional monolayer culture. This microfabricated chip could therefore serve as a novel culture platform for various cell-based assays, including those used in drug screening, basic biological studies, and tissue engineering applications.
Figures
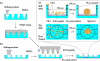



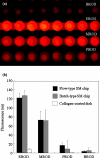
Similar articles
-
Fabrication of Concave Microwells and Their Applications in Micro-Tissue Engineering: A Review.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Sep 19;13(9):1555. doi: 10.3390/mi13091555. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36144178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Floating or adherent hepatocyte spheroid cultures using microwell chips with polyethylene glycol or polyimide surfaces.Biomed Mater. 2025 Mar 31;20(3). doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/adc17d. Biomed Mater. 2025. PMID: 40096815
-
Micropatterned culture of HepG2 spheroids using microwell chip with honeycomb-patterned polymer film.J Biosci Bioeng. 2014 Oct;118(4):455-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2014.03.006. Epub 2014 Apr 16. J Biosci Bioeng. 2014. PMID: 24742630
-
Advanced micromachining of concave microwells for long term on-chip culture of multicellular tumor spheroids.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014 Jun 11;6(11):8090-7. doi: 10.1021/am500367h. Epub 2014 May 19. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014. PMID: 24773458
-
Hepatocyte spheroid culture on a polydimethylsiloxane chip having microcavities.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2006;17(8):859-73. doi: 10.1163/156856206777996853. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2006. PMID: 17024877
Cited by
-
Recent advances in 2D and 3D in vitro systems using primary hepatocytes, alternative hepatocyte sources and non-parenchymal liver cells and their use in investigating mechanisms of hepatotoxicity, cell signaling and ADME.Arch Toxicol. 2013 Aug;87(8):1315-530. doi: 10.1007/s00204-013-1078-5. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Arch Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23974980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Strategies to Vascularize 3D Physiologically Relevant Models.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Oct;8(19):e2100798. doi: 10.1002/advs.202100798. Epub 2021 Aug 5. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34351702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fabrication of Concave Microwells and Their Applications in Micro-Tissue Engineering: A Review.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Sep 19;13(9):1555. doi: 10.3390/mi13091555. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36144178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in Engineered Human Liver Platforms for Drug Metabolism Studies.Drug Metab Dispos. 2018 Nov;46(11):1626-1637. doi: 10.1124/dmd.118.083295. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Drug Metab Dispos. 2018. PMID: 30135245 Free PMC article.
-
On-chip three-dimensional tumor spheroid formation and pump-less perfusion culture using gravity-driven cell aggregation and balanced droplet dispensing.Biomicrofluidics. 2012 Jul 24;6(3):34107. doi: 10.1063/1.4739460. Print 2012 Sep. Biomicrofluidics. 2012. PMID: 23882300 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nakazawa K., Ijima H., Fukuda J., Sakiyama R., Yamashita Y., Shimada M., Shirabe K., Tsujita E., Sugimachi K., and Funatsu K., Int. J. Artif. Organs IJAODS 25, 51 (2002). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
