p16( INK4a) positively regulates cyclin D1 and E2F1 through negative control of AUF1
- PMID: 21799732
- PMCID: PMC3140473
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0021111
p16( INK4a) positively regulates cyclin D1 and E2F1 through negative control of AUF1
Abstract
Background: The cyclin-D/CDK4,6/p16(INK4a)/pRB/E2F pathway, a key regulator of the critical G1 to S phase transition of the cell cycle, is universally disrupted in human cancer. However, the precise function of the different members of this pathway and their functional interplay are still not well defined.
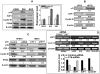
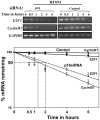
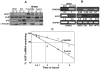
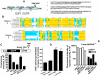
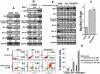
Methodology/principal findings: We have shown here that the tumor suppressor p16(INK4a) protein positively controls the expression of cyclin D1 and E2F1 in both human and mouse cells. p16(INK4a) stabilizes the mRNAs of the corresponding genes through negative regulation of the mRNA decay-promoting AUF1 protein. Immunoprecipitation of AUF1-associated RNAs followed by RT-PCR indicated that endogenous AUF1 binds to the cyclin D1 and E2F1 mRNAs. Furthermore, AUF1 down-regulation increased the expression levels of these genes, while concurrent silencing of AUF1 and p16(INK4a), using specific siRNAs, restored normal expression of both cyclinD1 and E2F1. Besides, we have shown the presence of functional AU-rich elements in the E2F1 3'UTR, which contributed to p16/AUF1-mediated regulation of E2F1 post-transcriptional events in vivo. Importantly, genome-wide gene expression microarray analysis revealed the presence of a large number of genes differentially expressed in a p16(INK4a) -dependent manner, and several of these genes are also members of the AUF1 and E2F1 regulons. We also present evidence that E2F1 mediates p16-dependent regulation of several pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins, and the consequent induction of spontaneous as well as doxorubicin-induced apoptosis.
Conclusion/significance: These findings show that the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16( INK4a) is also a modulator of transcription and apoptosis through controlling the expression of two major transcription regulators, AUF1 and E2F1.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. Cancer genes and the pathways they control. Nat Med. 2004;10:789–799. - PubMed
-
- Nevins JR. The Rb/E2F pathway and cancer. Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10:699–703. - PubMed
-
- Kaye FJ. RB and cyclin dependent kinase pathways: defining a distinction between RB and p16 loss in lung cancer. Oncogene. 2002;21:6908–6914. - PubMed
-
- Giacinti C, Giordano A. RB and cell cycle progression. Oncogene. 2006;25:5220–5227. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

