Social transmission and the spread of modern contraception in rural Ethiopia
- PMID: 21799882
- PMCID: PMC3142194
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022515
Social transmission and the spread of modern contraception in rural Ethiopia
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2011;6(8). doi: 10.1371/annotation/d4ace6be-2089-47e8-86b2-42d04189324a
Abstract
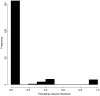
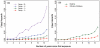
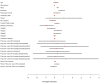
Socio-economic development has proven to be insufficient to explain the time and pace of the human demographic transition. Shifts to low fertility norms have thus been thought to result from social diffusion, yet to date, micro-level studies are limited and are often unable to disentangle the effect of social transmission from that of extrinsic factors. We used data which included the first ever use of modern contraception among a population of over 900 women in four villages in rural Ethiopia, where contraceptive prevalence is still low (<20%). We investigated whether the time of adoption of modern contraception is predicted by (i) the proportion of ever-users/non ever-users within both women and their husbands' friendships networks and (ii) the geographic distance to contraceptive ever-users. Using a model comparison approach, we found that individual socio-demographic characteristics (e.g. parity, education) and a religious norm are the most likely explanatory factors of temporal and spatial patterns of contraceptive uptake, while the role of person-to-person contact through either friendship or spatial networks remains marginal. Our study has broad implications for understanding the processes that initiate transitions to low fertility and the uptake of birth control technologies in the developing world.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Lee R. The demographic transition: three centuries of fundamental change. Journal of Economic Perspectives. 2003;17:167–190.
-
- Mason KO. Explaining fertility transitions. Demography. 1997;34:443–454. - PubMed
-
- Borgerhoff-Mulder M. The demographic transition: are we any closer to an evolutionary explanation? Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 1998;13:266–270. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan H, Lancaster JB, Bock JA, Johnson SE. Does observed fertility maximize fitness among New Mexican men? A test of an optimality model and a new theory of parental investment in the embodied capital of offspring. Human Nature. 1995;6:325–360. - PubMed
-
- Hill SE, Reeve HK. Low fertility in humans as the evolutionary outcome of snowballing resource games. Behavioural Ecology and Sociobiology. 2005;16:398–402.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

