SEAS: a system for SEED-based pathway enrichment analysis
- PMID: 21799897
- PMCID: PMC3142180
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022556
SEAS: a system for SEED-based pathway enrichment analysis
Abstract
Pathway enrichment analysis represents a key technique for analyzing high-throughput omic data, and it can help to link individual genes or proteins found to be differentially expressed under specific conditions to well-understood biological pathways. We present here a computational tool, SEAS, for pathway enrichment analysis over a given set of genes in a specified organism against the pathways (or subsystems) in the SEED database, a popular pathway database for bacteria. SEAS maps a given set of genes of a bacterium to pathway genes covered by SEED through gene ID and/or orthology mapping, and then calculates the statistical significance of the enrichment of each relevant SEED pathway by the mapped genes. Our evaluation of SEAS indicates that the program provides highly reliable pathway mapping results and identifies more organism-specific pathways than similar existing programs. SEAS is publicly released under the GPL license agreement and freely available at http://csbl.bmb.uga.edu/~xizeng/research/seas/.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
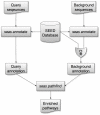
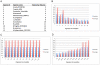
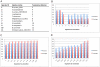
References
-
- Metzker ML. Sequencing technologies - the next generation. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:31–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

