Neurogenesis at the brain-cerebrospinal fluid interface
- PMID: 21801012
- PMCID: PMC3777264
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-092910-154026
Neurogenesis at the brain-cerebrospinal fluid interface
Abstract
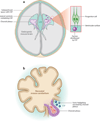
Cerebral cortical progenitor cells can be classified into several different types, and each progenitor type integrates cell-intrinsic and cell-extrinsic cues to regulate neurogenesis. On one hand, cell-intrinsic mechanisms that depend upon appropriate apical-basal polarity are established by adherens junctions and apical complex proteins and are particularly important in progenitors with apical processes contacting the lateral ventricle. The apical protein complexes themselves are concentrated at the ventricular surface, and apical complex proteins regulate mitotic spindle orientation and cell fate. On the other hand, remarkably little is known about how cell-extrinsic cues signal to progenitors and couple with cell-intrinsic mechanisms to instruct neurogenesis. Recent research shows that the cerebrospinal fluid, which contacts apical progenitors at the ventricular surface and bathes the apical complex of these cells, provides growth- and survival-promoting cues for neural progenitor cells in developing and adult brain. This review addresses how the apical-basal polarity of progenitor cells regulates cell fate and allows progenitors to sample diffusible signals distributed by the cerebrospinal fluid. We also review several classes of signaling factors that the cerebrospinal fluid distributes to the developing brain to instruct neurogenesis.
Figures



References
LITERATURE CITED
-
- Aaku-Saraste E, Oback B, Hellwig A, Huttner WB. Neuroepithelial cells downregulate their plasma membrane polarity prior to neural tube closure and neurogenesis. Mech. Dev. 1997;69:71–81. - PubMed
-
- Agnati LF, Zoli M, Stromberg I, Fuxe K. Intercellular communication in the brain: wiring versus volume transmission. Neuroscience. 1995;69:711–726. - PubMed
-
- Angevine JB, Jr., Bodian D, Coulombre AJ, Edds MVJr, Hamburger V, et al. Embryonic vertebrate central nervous system: revised terminology. Anat. Rec. 1970;166:257–261. - PubMed
-
- Awatramani R, Soriano P, Rodriguez C, Mai JJ, Dymecki SM. Cryptic boundaries in roof plate and choroid plexus identified by intersectional gene activation. Nat. Genet. 2003;35:70–75. - PubMed
-
- Baker J, Liu JP, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A. Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell. 1993;75:73–82. - PubMed
RELATED RESOURCES
-
- He S, Nahada D, Morrison SJ. Mechanisms of stem cell self-renewal. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2009;25:377–406. - PubMed
-
- Jackson Lab. Hydrocephalus in laboratory mice. JAX® NOTES. 2003:490. http://jaxmice.jax.org/jaxnotes/archive/490f.html.
-
- Sundberg JP, Woolcott BL, Cunlifee-Beamer T, Brown KS, Bronson R. Spontaneous hydrocephalus in inbred strains of mice. JAX® NOTES. 1991:445. http://jaxmice.jax.org/jaxnotes/archive/445a.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

