Investigating a pathogenic role for TXNDC5 in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 21801346
- PMCID: PMC3239364
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3429
Investigating a pathogenic role for TXNDC5 in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: Expression of TXNDC5, which is induced by hypoxia, stimulates cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Our previous study detected increased TXNDC5 expression in the synovial tissues of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients using proteomic methods. The current study investigated a pathogenic role for TXNDC5 in RA.
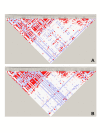
Method: Expression of TXNDC5 in synovial membranes was quantitatively analyzed by immunohistochemistry, Western blotting and real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Serum TXNDC5 levels and serum anti-TXNDC5 antibody levels were determined using sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). A total of 96 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in or near the TXNDC5 gene were genotyped using custom-designed Illumina 96-SNP VeraCode microassay. Allele frequencies and genotype frequencies of SNPs were assessed using a case-control design in a cohort of 267 Chinese patients with RA, 51 patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and 160 healthy controls. Additional genotyping of 951 patients with RA and 898 healthy controls was performed for four SNPs (rs2277105, rs369086, rs443861 and rs11962800) using the TaqMan method.
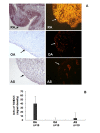
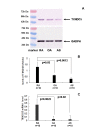
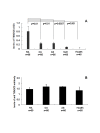
Results: Real-time PCR, Western blotting and immunohistochemistry detected significantly higher TXNDC5 expression in the synovial tissues of RA patients compared to samples from patients with osteoarthritis (OA) or AS. ELISA detected significantly higher levels of TXNDC5 in the blood of RA patients compared to OA, AS and systemic lupus erythematosus patients, and healthy controls. ELISA did not detect significantly different levels of anti-TXNDC5 antibody in the blood of RA, OA and AS patients and healthy controls. A total of 9 SNPs (rs9505298, rs41302895, rs1225936, rs1225938, rs372578, rs443861, rs408014, rs9392189 and rs2743992) showed significant association with RA, while 16 SNPs (rs1044104, rs1225937, rs1225938, rs372578, rs89715, rs378963, rs1225944, rs1225947, rs1238994, rs369086, rs408014, rs368074, rs1225954, rs1225955, rs13209404 and rs3812162) showed significant association with AS. Taqman SNP assay demonstrated that rs443861 has an association with RA, which correlates with the microassay results.
Conclusions: TXNDC5 is up-regulated in synovial tissues of RA patients. TXNDC5 has a genetic effect on the risk of RA and AS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role and mechanism of TXNDC5 in diseases.Eur J Med Res. 2022 Aug 8;27(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s40001-022-00770-4. Eur J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35934705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of proteins with increased expression in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissues.J Rheumatol. 2009 May;36(5):872-80. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.080939. Epub 2009 Apr 15. J Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19369474
-
Inhibition of PCSK6 may play a protective role in the development of rheumatoid arthritis.J Rheumatol. 2015 Feb;42(2):161-9. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.140435. Epub 2014 Nov 29. J Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25433529
-
Investigating a pathogenic role for TXNDC5 in tumors.Int J Oncol. 2013 Dec;43(6):1871-84. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.2123. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24100949
-
The role and mechanism of TXNDC5 in disease progression.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 2;15:1354952. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1354952. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38629066 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteins involved in the endoplasmic reticulum stress are modulated in synovitis of osteoarthritis, chronic pyrophosphate arthropathy and rheumatoid arthritis, and correlate with the histological inflammatory score.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 4;10(1):14159. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70803-7. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32887899 Free PMC article.
-
TXNDC5 protects synovial fibroblasts of rheumatoid arthritis from the detrimental effects of endoplasmic reticulum stress.Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2020 Feb;9(1):23-29. doi: 10.5582/irdr.2019.01139. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2020. PMID: 32201671 Free PMC article.
-
Investigate pathogenic mechanism of TXNDC5 in rheumatoid arthritis.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53301. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0053301. Epub 2013 Jan 9. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23326410 Free PMC article.
-
TXNDC5 is a cervical tumor susceptibility gene that stimulates cell migration, vasculogenic mimicry and angiogenesis by down-regulating SERPINF1 and TRAF1 expression.Oncotarget. 2017 Jun 29;8(53):91009-91024. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18857. eCollection 2017 Oct 31. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29207620 Free PMC article.
-
The role and mechanism of TXNDC5 in diseases.Eur J Med Res. 2022 Aug 8;27(1):145. doi: 10.1186/s40001-022-00770-4. Eur J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35934705 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

