Osteoprotegerin and coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetic patients with microalbuminuria
- PMID: 21801376
- PMCID: PMC3162489
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2840-10-70
Osteoprotegerin and coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetic patients with microalbuminuria
Abstract
Objective: Plasma osteoprotegerin (P-OPG) is an independent predictor of cardiovascular disease in diabetic and other populations. OPG is a bone-related glycopeptide produced by vascular smooth muscle cells and increased P-OPG may reflect arterial damage. We investigated the correlation between P-OPG and coronary artery disease (CAD) in asymptomatic type 2 diabetic patients with microalbuminuria.
Methods: P-OPG was measured in 200 asymptomatic diabetic patients without known cardiac disease. Patients with P-NT-proBNP >45.2 ng/l and/or coronary calcium score (CCS) ≥400 were stratified as high risk of CAD (n = 133), and all other patients as low risk patients (n = 67). High risk patients were examined by myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI; n = 109), and/or CT-angiography (n = 20), and/or coronary angiography (CAG; n = 86). Significant CAD was defined by presence of significant myocardial perfusion defects at MPI and/or >70% coronary artery stenosis at CAG.
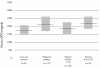
Results: Significant CAD was demonstrated in 70 of the high risk patients and of these 23 patients had >70% coronary artery stenosis at CAG. Among high risk patients, increased P-OPG was an independent predictor of significant CAD (adjusted odds ratio [CI] 3.11 [1.01-19.54] and 3.03 [1.00-9.18] for second and third tertile vs.first tertile P-OPG, respectively) and remained so after adjustments for NT-proBNP and CCS. High P-OPG was also associated with presence of >70% coronary artery stenosis(adjusted odds ratio 14.20 [1.35-148.92] for third vs. first tertile P-OPG), and 91% of patients with low (first tertile) P-OPG did not have >70% coronary artery stenosis.
Conclusions: Elevated P-OPG is an independent predictor of the presence of CAD in asymptomatic type 2 diabetic patients with microalbuminuria.
Figures
References
-
- Ninomiya T, Perkovic V, de Galan BE, Zoungas S, Pillai A, Jardine M, Patel A, Cass A, Neal B, Poulter N, Mogensen CE, Cooper M, Marre M, Williams B, Hamet P, Mancia G, Woodward M, MacMahon S, Chalmers J. Albuminuria and kidney function independently predict cardiovascular and renal outcomes in diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20:1813–1821. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008121270. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jorsal A, Tarnow L, Flyvbjerg A, Parving HH, Rossing P, Rasmussen LM. Plasma osteoprotegerin levels predict cardiovascular and all-cause mortality and deterioration of kidney function in type 1 diabetic patients with nephropathy. Diabetologia. 2008;51:2100–2107. doi: 10.1007/s00125-008-1123-8. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

