Increasing levels of circulating Th17 cells and interleukin-17 in rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to anti-TNF-α therapy
- PMID: 21801431
- PMCID: PMC3239366
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3431
Increasing levels of circulating Th17 cells and interleukin-17 in rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to anti-TNF-α therapy
Abstract
Introduction: The objective of this study was to investigate the effects of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α inhibitors on circulating T helper-type 17 (Th17) cells and Th17-related cytokines in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: The frequencies of circulating Th17 cells and serum levels of Th17-related cytokines were determined using flow cytometry analysis and ELISA, respectively, in 48 RA patients both before (baseline) and six months after anti-TNF-α therapy. Therapeutic response was evaluated using European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR) response criteria.
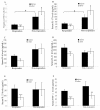
Results: Significantly higher baseline frequencies of circulating Th17 cells and serum levels of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-17, IL-21, IL-23 and TNF-α were observed in active RA patients than in 12 healthy controls (all P < 0.001). After anti-TNF-α therapy, 36 patients (75%) were EULAR responders (20 good responders and 16 moderate responders) and 12 (25.0%) were non-responders. The mean levels of circulating Th17 cells and IL-17 significantly decreased (1.13% vs. 0.79%; 43.1 pg/ml vs. 27.8 pg/ml; respectively, both P < 0.001) in parallel with clinical remission in responders. Levels of IL-6, IL-21, IL-23 and TNF-α were significantly decreased after anti-TNF-α therapy in responders. In contrast, the mean levels of circulating Th17 cells and IL-17 significantly increased after anti-TNF-α therapy (2.94% vs. 4.23%; 92.1 pg/ml vs. 148.6 pg/ml; respectively, both P < 0.05) in non-responders. Logistic regression analysis identified a high baseline level of IL-17 as a significant predictor of poor therapeutic response.
Conclusions: The beneficial effect of anti-TNF-α therapy might involve a decrease in Th17-related cytokines in responders, whereas rising levels of circulating Th17-cells and IL-17 were observed in patients with an inadequate response to anti-TNF-α therapy.
Figures

References
-
- van der Heijde D, Klareskog L, Rodriguez-Valverde V, Codreanu C, Bolosiu H, Melo-Gomes J, Tornero-Molina J, Wajdula J, Pedersen R, Fatenejad S. TEMPO Study Investigators. Comparison of etanercept and methotrexate, alone and combined, in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: Two-year clinical and radiographic results from the TEMPO study, a double-blind, randomized trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:1063–1074. doi: 10.1002/art.21655. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, Cohen SB, Pavelka K, van Vollenhoven R, Sharp J, Perez JL, Spencer-Green GT. The PREMIER study: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical trial of combination therapy with adalimumab plus methotrexate versus methotrexate alone or adalimumab alone in patients with early, aggressive rheumatoid arthritis who had not had previous methotrexate treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:26–37. doi: 10.1002/art.21519. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

