Essential role of caspase-8 in p53/p73-dependent apoptosis induced by etoposide in head and neck carcinoma cells
- PMID: 21801448
- PMCID: PMC3160414
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-95
Essential role of caspase-8 in p53/p73-dependent apoptosis induced by etoposide in head and neck carcinoma cells
Abstract
Background: Caspase-8 is a key upstream mediator in death receptor-mediated apoptosis and also participates in mitochondria-mediated apoptosis via cleavage of proapoptotic Bid. However, the role of caspase-8 in p53- and p73-dependent apoptosis induced by genotoxic drugs remains unclear. We recently reported that the reconstitution of procaspase-8 is sufficient for sensitizing cisplatin- but not etoposide-induced apoptosis, in chemoresistant and caspase-8 deficient HOC313 head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) cells.
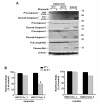
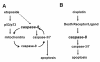
Results: We show that p53/p73-dependent caspase-8 activation is required for sensitizing etoposide-induced apoptosis by utilizing HOC313 cells carrying a temperature-sensitive p53G285K mutant. Restoration of wild-type p53 function under the permissive conditions, together with etoposide treatment, led to substantial transcriptional activation of proapoptotic Noxa and PUMA, but failed to induce apoptosis. In addition to p53 restoration, caspase-8 reconstitution was needed for sensitization to etoposide-induced apoptosis, mitochondria depolarization, and cleavage of the procaspases-3, and -9. In etoposide-sensitive Ca9-22 cells carrying a temperature-insensitive mutant p53, siRNA-based p73 knockdown blocked etoposide-induced apoptosis and procaspase-8 cleavage. However, induction of p73 protein and up-regulation of Noxa and PUMA, although observed in Ca9-22 cells, were hardly detected in etoposide-treated HOC313 cells under non-permissive conditions, suggesting a contribution of p73 reduction to etoposide resistance in HOC313 cells. Finally, the caspase-9 inhibitor Ac-LEHD-CHO or caspase-9 siRNA blocked etoposide-induced caspase-8 activation, Bid cleavage, and apoptosis in both cell lines, indicating that p53/p73-dependent caspase-8 activation lies downstream of mitochondria.
Conclusions: we conclude that p53 and p73 can act as upstream regulators of caspase-8, and that caspase-8 is an essential mediator of the p53/p73-dependent apoptosis induced by etoposide in HNSCC cells. Our data suggest the importance of caspase-8-mediated positive feedback amplification in the p53/p73-dependent apoptosis induced by etoposide in HNSCC cells.
Figures






Similar articles
-
α-TEA cooperates with chemotherapeutic agents to induce apoptosis of p53 mutant, triple-negative human breast cancer cells via activating p73.Breast Cancer Res. 2011 Jan 7;13(1):R1. doi: 10.1186/bcr2801. Breast Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21214929 Free PMC article.
-
p63 mediates survival in squamous cell carcinoma by suppression of p73-dependent apoptosis.Cancer Cell. 2006 Jan;9(1):45-56. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2005.12.013. Cancer Cell. 2006. PMID: 16413471
-
CK2 phosphorylates and inhibits TAp73 tumor suppressor function to promote expression of cancer stem cell genes and phenotype in head and neck cancer.Neoplasia. 2014 Oct 23;16(10):789-800. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2014.08.014. eCollection 2014 Oct. Neoplasia. 2014. PMID: 25379016 Free PMC article.
-
P53 family: at the crossroads in cancer therapy.Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(32):4328-44. doi: 10.2174/092986709789578196. Curr Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19754415 Review.
-
Role of p73 in malignancy: tumor suppressor or oncogene?Cell Death Differ. 2002 Mar;9(3):237-45. doi: 10.1038/sj.cdd.4400995. Cell Death Differ. 2002. PMID: 11859406 Review.
Cited by
-
Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles for Cancer Therapy and In Vivo Bioimaging.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 4;13(23):6114. doi: 10.3390/cancers13236114. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34885224 Free PMC article.
-
AKT is indispensable for coordinating Par-4/JNK cross talk in p21 downmodulation during ER stress.Oncogenesis. 2017 May 22;6(5):e341. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2017.41. Oncogenesis. 2017. PMID: 28530706 Free PMC article.
-
ENCoRE: an efficient software for CRISPR screens identifies new players in extrinsic apoptosis.BMC Genomics. 2017 Nov 25;18(1):905. doi: 10.1186/s12864-017-4285-2. BMC Genomics. 2017. PMID: 29178829 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of Rad9 at serine 328 by cyclin A-Cdk2 triggers apoptosis via interfering Bcl-xL.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e44923. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0044923. Epub 2012 Sep 13. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23028682 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Activity of N-Hydroxyethyl-4-aza-2,3-didehydropodophyllotoxin Derivatives upon Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Cells.Open J Med Chem. 2014 Mar;4(1):1-11. doi: 10.4236/ojmc.2014.41001. Open J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25554737 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM. Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science. 1998;281:1305–1308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

