Sox2 and Fgf interact with Atoh1 to promote sensory competence throughout the zebrafish inner ear
- PMID: 21801718
- PMCID: PMC3171634
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.07.019
Sox2 and Fgf interact with Atoh1 to promote sensory competence throughout the zebrafish inner ear
Abstract
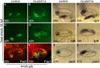
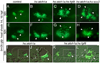
Atoh1 is required for differentiation of sensory hair cells in the vertebrate inner ear. Moreover, misexpression of Atoh1 is sufficient to establish ectopic sensory epithelia, making Atoh1 a good candidate for gene therapy to restore hearing. However, competence to form sensory epithelia appears to be limited to discrete regions of the inner ear. To better understand the developmental factors influencing sensory-competence, we examined the effects of misexpressing atoh1a in zebrafish embryos under various developmental conditions. Activation of a heat shock-inducible transgene, hs:atoh1a, resulted in ectopic expression of early markers of sensory development within 2h, and mature hair cells marked by brn3c:GFP began to accumulate 9h after heat shock. The ability of atoh1a to induce ectopic sensory epithelia was maximal when activated during placodal or early otic vesicle stages but declined rapidly thereafter. At no stage was atoh1a sufficient to induce sensory development in dorsal or lateral non-sensory regions of the otic vesicle. However, co-misexpression of atoh1a with fgf3, fgf8 or sox2, genes normally acting in the same gene network with atoh1a, stimulated sensory development in all regions of the otic vesicle. Thus, expression of fgf3, fgf8 or sox2 strongly enhances competence to respond to Atoh1.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
sox2 and sox3 Play unique roles in development of hair cells and neurons in the zebrafish inner ear.Dev Biol. 2018 Mar 1;435(1):73-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.01.010. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29355523 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish atoh1 genes: classic proneural activity in the inner ear and regulation by Fgf and Notch.Development. 2007 Jan;134(2):295-305. doi: 10.1242/dev.02734. Epub 2006 Dec 13. Development. 2007. PMID: 17166920
-
Fgf8 and Fgf3 are required for zebrafish ear placode induction, maintenance and inner ear patterning.Mech Dev. 2002 Nov;119(1):91-108. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(02)00343-x. Mech Dev. 2002. PMID: 12385757
-
Atoh1 and other related key regulators in the development of auditory sensory epithelium in the mammalian inner ear: function and interplay.Dev Biol. 2019 Feb 15;446(2):133-141. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.12.025. Epub 2018 Dec 31. Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 30605626 Review.
-
[Roles of the FGF signaling pathway in regulating inner ear development and hair cell regeneration].Yi Chuan. 2018 Jul 20;40(7):515-524. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.17-407. Yi Chuan. 2018. PMID: 30021715 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
In vivo generation of immature inner hair cells in neonatal mouse cochleae by ectopic Atoh1 expression.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 20;9(2):e89377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089377. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586731 Free PMC article.
-
Fgf3 and Fgf16 expression patterns define spatial and temporal domains in the developing chick inner ear.Brain Struct Funct. 2017 Jan;222(1):131-149. doi: 10.1007/s00429-016-1205-1. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Brain Struct Funct. 2017. PMID: 26995070 Free PMC article.
-
Dual role for Sox2 in specification of sensory competence and regulation of Atoh1 function.Dev Neurobiol. 2017 Jan;77(1):3-13. doi: 10.1002/dneu.22401. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Dev Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27203669 Free PMC article.
-
Segregating neural and mechanosensory fates in the developing ear: patterning, signaling, and transcriptional control.Cell Tissue Res. 2015 Jan;359(1):315-32. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-1917-6. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Cell Tissue Res. 2015. PMID: 24902666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative assessment of Fgf's diverse roles in inner ear development: A zebrafish perspective.Dev Dyn. 2021 Nov;250(11):1524-1551. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.343. Epub 2021 Apr 19. Dev Dyn. 2021. PMID: 33830554 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alsina B, Abelló G, Ulloa E, Henrique D, Pujades C, Giraldez F. FGF signaling is required for determination of otic neuroblasts in the chick embryo. Dev. Biol. 2004;267:119–134. - PubMed
-
- Brooker R, Hozumi K, Lewis J. Notch ligands with contrasting functions: Jagged1 and Delta1 in the mouse inner ear. Development. 2006;133:1277–1286. - PubMed
-
- Chen P, Johnson JE, Zoghbi HY, Segil N. The role of Math1 in inner ear development: Uncoupling the establishment of the sensory primordium from hair cell fate determination. Development. 2002;129:2495–2505. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

