Protein expressions and genetic variations of SLC5A8 in prostate cancer risk and aggressiveness
- PMID: 21802122
- PMCID: PMC3190039
- DOI: 10.1016/j.urology.2011.04.055
Protein expressions and genetic variations of SLC5A8 in prostate cancer risk and aggressiveness
Abstract
Objective: To understand the role in prostate cancer risk and aggressiveness, we investigated the expression in prostate tumor and single nucleotide polymorphisms of SLC5A8. Previous studies have suggested that SLC5A8 might function as a tumor suppressor gene, whose silencing by epigenetic changes might contribute to carcinogenesis.
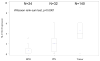
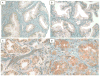
Methods: We constructed tissue microarrays from 183 prostate tumor tissues, 43 adjacent non-neoplastic tissues from the same patients, and 13 tissue samples from patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia or prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. A semiquantitative assessment of SLC5A8 protein expression was determined as the product of immunostaining intensity and the percentage of cells stained. In addition, we compared the frequencies of 4 single nucleotide polymorphisms (rs164365, rs1709189, rs1399236, and rs1681096) in SLC5A8 between 668 prostate cancer cases and 385 controls.
Results: SLC5A8 expression was significantly greater in the tumor tissues than in the paired non-neoplastic tissues (P < .0001). In the Moffitt samples, we observed a borderline moderate risk increase in patients with a genotype containing ≥1 "A" allele of rs164365 (odds ratio 1.35, 95% confidence interval 1.00-1.80), especially among tall men (≥70 in.; odds ratio 1.80, 95% confidence interval 1.20-2.68). However, these results were not confirmed in the Cancer Genetic Markers of Susceptibility population.
Conclusion: These data suggest that the expression pattern of SLC5A8 might be used as a diagnostic biomarker, and a larger study is required to assess the importance of SLC5A8 single nucleotide polymorphisms in prostate cancer.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Wright EM, Turk E. The sodium/glucose cotransport family SLC5. Pflugers Arch. 2004;447:510–8. - PubMed
-
- Gopal E, Miyauchi S, Martin PM, Ananth S, Roon P, Smith SB, Ganapathy V. Transport of Nicotinate and Structurally Related Compounds by Human SMCT1 (SLC5A8) and Its Relevance to Drug Transport in the Mammalian Intestinal Tract. Pharm Res. 2007 - PubMed
-
- Martin PM, Gopal E, Ananth S, Zhuang L, Itagaki S, Prasad BM, Smith SB, Prasad PD, Ganapathy V. Identity of SMCT1 (SLC5A8) as a neuron-specific Na+-coupled transporter for active uptake of L-lactate and ketone bodies in the brain. J Neurochem. 2006;98:279–88. - PubMed
-
- Gupta N, Martin PM, Prasad PD, Ganapathy V. SLC5A8 (SMCT1)-mediated transport of butyrate forms the basis for the tumor suppressive function of the transporter. Life Sci. 2006;78:2419–25. - PubMed
-
- Thangaraju M, Gopal E, Martin PM, Ananth S, Smith SB, Prasad PD, Sterneck E, Ganapathy V. SLC5A8 triggers tumor cell apoptosis through pyruvate-dependent inhibition of histone deacetylases. Cancer Res. 2006;66:11560–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

