CXCL10/IP-10 in infectious diseases pathogenesis and potential therapeutic implications
- PMID: 21802343
- PMCID: PMC3203691
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2011.06.001
CXCL10/IP-10 in infectious diseases pathogenesis and potential therapeutic implications
Abstract
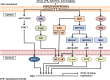
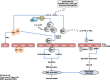
C-X-C motif chemokine 10 (CXCL10) also known as interferon γ-induced protein 10 kDa (IP-10) or small-inducible cytokine B10 is a cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family. CXCL10 binds CXCR3 receptor to induce chemotaxis, apoptosis, cell growth and angiostasis. Alterations in CXCL10 expression levels have been associated with inflammatory diseases including infectious diseases, immune dysfunction and tumor development. CXCL10 is also recognized as a biomarker that predicts severity of various diseases. A review of the emerging role of CXCL10 in pathogenesis of infectious diseases revealed diverse roles of CXCL10 in disease initiation and progression. The potential utilization of CXCL10 as a therapeutic target for infectious diseases is discussed.
Copyright © 2011. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

