Efficacy of novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, AR42, in a mouse model of, human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 adult T cell lymphoma
- PMID: 21802726
- PMCID: PMC3191315
- DOI: 10.1016/j.leukres.2011.07.015
Efficacy of novel histone deacetylase inhibitor, AR42, in a mouse model of, human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 adult T cell lymphoma
Abstract
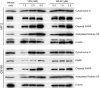
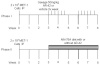
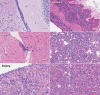
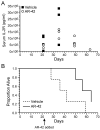
Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1) causes a variety of forms of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL), a refractory CD4+/CD25+ T-cell malignancy. Novel approaches to treat ATL patients are required due to the resistance of ATL to conventional chemotherapies. Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi), which induce histone hyperacetylation leading to chromatin remodeling and reactivation of transcriptionally repressed genes have shown efficacy against a variety of cancers. Herein, we tested if valproic acid and the novel orally bioavailable HDACi, AR-42 reduced the proliferation of ATL cell lines by promoting apoptosis and histone hyperacetylation. Both compounds were cytotoxic and elicited a dose dependent increase in cytochrome C and cleaved Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) indicating the induction of cell death by apoptosis and promoted acetylation of histone H3 in both MT-2 and C8166 cell lines. We then evaluated the effects of AR-42, for survival in an ATL NOD/SCID mouse model. A dietary formulation of AR-42 prolonged survival of ATL engrafted mice compared to controls. Our data provide new directions for the treatment of ATL and support the further development of AR-42 against HTLV-1-associated lymphoid malignancies.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Inhibiting HDACs in a preclinical model of HTLV-1-induced adult T-cell lymphoma.Leuk Res. 2011 Nov;35(11):1436-7. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2011.07.036. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Leuk Res. 2011. PMID: 21868093 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Inhibiting HDACs in a preclinical model of HTLV-1-induced adult T-cell lymphoma.Leuk Res. 2011 Nov;35(11):1436-7. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2011.07.036. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Leuk Res. 2011. PMID: 21868093 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Effective treatment of a murine model of adult T-cell leukemia using depsipeptide and its combination with unmodified daclizumab directed toward CD25.Blood. 2009 Feb 5;113(6):1287-93. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-04-149658. Epub 2008 Oct 23. Blood. 2009. PMID: 18948574 Free PMC article.
-
CDK9 Inhibitor Induces Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Suppression of Tumor Growth in Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma.Biol Pharm Bull. 2023;46(9):1269-1276. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b23-00228. Biol Pharm Bull. 2023. PMID: 37661406
-
Treatment of adult T-cell leukaemia/lymphoma: is the virus a target?Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2015 Dec;28(6):583-8. doi: 10.1097/QCO.0000000000000207. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2015. PMID: 26381999 Review.
-
[New treatment strategy for adult T-cell leukemia targeting for anti-tumor immunity and a longevity gene-encoded protein].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2011;131(7):1061-72. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.131.1061. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2011. PMID: 21720136 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Animals Models of Human T Cell Leukemia Virus Type I Leukemogenesis.ILAR J. 2016;57(1):3-11. doi: 10.1093/ilar/ilv045. ILAR J. 2016. PMID: 27034390 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitor AR-42 inhibits breast cancer cell growth and demonstrates a synergistic effect in combination with 5-FU.Oncol Lett. 2018 Aug;16(2):1967-1974. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8854. Epub 2018 May 31. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30008890 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, AR-42, Reactivates HIV-1 from Chronically and Latently Infected CD4+ T-cells.Retrovirology (Auckl). 2015;7:1-5. doi: 10.4137/RRT.S31632. Epub 2015 Oct 15. Retrovirology (Auckl). 2015. PMID: 26855567 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting HDACs in a preclinical model of HTLV-1-induced adult T-cell lymphoma.Leuk Res. 2011 Nov;35(11):1436-7. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2011.07.036. Epub 2011 Aug 24. Leuk Res. 2011. PMID: 21868093 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Adult T-Cell Leukemia: a Comprehensive Overview on Current and Promising Treatment Modalities.Curr Oncol Rep. 2021 Nov 4;23(12):141. doi: 10.1007/s11912-021-01138-3. Curr Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34735653 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

