Restraint of Fgf8 signaling by retinoic acid signaling is required for proper heart and forelimb formation
- PMID: 21803036
- PMCID: PMC3171575
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2011.07.022
Restraint of Fgf8 signaling by retinoic acid signaling is required for proper heart and forelimb formation
Abstract
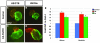
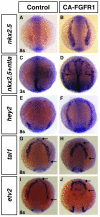
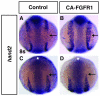
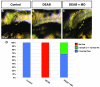
Cardiomelic or heart-hand syndromes include congenital defects affecting both the forelimb and heart, suggesting a hypothesis where similar signals may coordinate their development. In support of this hypothesis, we have recently defined a mechanism by which retinoic acid (RA) signaling acts on the forelimb progenitors to indirectly restrict cardiac cell number. However, we still do not have a complete understanding of the mechanisms downstream of RA signaling that allow for the coordinated development of these structures. Here, we test the hypothesis that appropriate Fgf signaling in the cardiac progenitor field downstream of RA signaling is required for the coordinated development of the heart and forelimb. Consistent with this hypothesis, we find that increasing Fgf signaling can autonomously increase cardiac cell number and non-autonomously inhibit forelimb formation over the same time period that embryos are sensitive to loss of RA signaling. Furthermore, we find that Fgf8a, which is expressed in the cardiac progenitors, is expanded into the posterior in RA signaling-deficient zebrafish embryos. Reducing Fgf8a function in RA signaling-deficient embryos is able to rescue both heart and forelimb development. Together, these results are the first to directly support the hypothesis that RA signaling is required shortly after gastrulation in the forelimb field to temper Fgf8a signaling in the cardiac field, thus coordinating the development of the heart and forelimb.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures







References
-
- Ahn DG, Kourakis MJ, Rohde LA, Silver LM, Ho RK. T-box gene tbx5 is essential for formation of the pectoral limb bud. Nature. 2002;417:754–758. - PubMed
-
- Alsan BH, Schultheiss TM. Regulation of avian cardiogenesis by Fgf8 signaling. Development. 2002;129:1935–1943. - PubMed
-
- Barron M, Gao M, Lough J. Requirement for BMP and FGF signaling during cardiogenic induction in non-precardiac mesoderm is specific, transient, and cooperative. Dev. Dyn. 2000;218:383–393. - PubMed
-
- Bruneau BG, Nemer G, Schmitt JP, Charron F, Robitaille L, Caron S, Conner DA, Gessler M, Nemer M, Seidman CE, Seidman JG. A murine model of Holt-Oram syndrome defines roles of the T-box transcription factor Tbx5 in cardiogenesis and disease. Cell. 2001;106:709–721. - PubMed
-
- Connors SA, Tucker JA, Mullins MC. Temporal and spatial action of tolloid (mini fin) and chordin to pattern tail tissues. Dev. Biol. 2006;293:191–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

