A diffusion tensor brain template for rhesus macaques
- PMID: 21803162
- PMCID: PMC3195880
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.07.029
A diffusion tensor brain template for rhesus macaques
Abstract
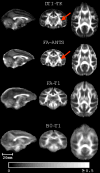
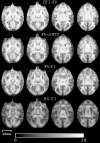
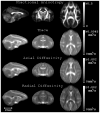
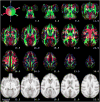
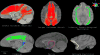
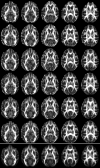
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is a powerful and noninvasive imaging method for characterizing tissue microstructure and white matter organization in the brain. While it has been applied extensively in research studies of the human brain, DTI studies of non-human primates have been performed only recently. The growing application of DTI in rhesus monkey studies would significantly benefit from a standardized framework to compare findings across different studies. A very common strategy for image analysis is to spatially normalize (co-register) the individual scans to a representative template space. This paper presents the development of a DTI brain template, UWRMAC-DTI271, for adolescent Rhesus Macaque (Macaca mulatta) monkeys. The template was generated from 271 rhesus monkeys, collected as part of a unique brain imaging genetics study. It is the largest number of animals ever used to generate a computational brain template, which enables the generation of a template that has high image quality and accounts for variability in the species. The quality of the template is further ensured with the use of DTI-TK, a well-tested and high-performance DTI spatial normalization method in human studies. We demonstrated its efficacy in monkey studies for the first time by comparing it to other commonly used scalar-methods for DTI normalization. It is anticipated that this template will play an important role in facilitating cross-site voxelwise DTI analyses in Rhesus Macaques. Such analyses are crucial in investigating the role of white matter structure in brain function, development, and other psychopathological disorders for which there are well-validated non-human primate models.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
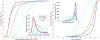

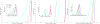
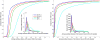
References
-
- Alexander DC, Gee JC. Spatial transformations for registration of DT-MRIs. Proc. Medical Image Understanding and Analysis; London. 2000a. pp. 203–206.
-
- Alexander DC, Gee JC. Elastic matching of diffusion tensor images. Comput Vis Image Underst. 2000b;77:233–250.
-
- Alexander DC, Pierpaoli C, Basser PJ, Gee JC. Spatial transformations of diffusion tensor magnetic resonance images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2001;20:1131–1139. - PubMed
-
- Alexander DC, Barker GJ. Optimal imaging parameters for fibre-orientation estimation in diffusion MRI. NeuroImage. 2005;27:357–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P30 HD003352/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH062015/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH084051/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R03 EB009321/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH080826/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH018931/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH46729/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH81884/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH084051/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH046729/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH62015/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R03-EB009321/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- MH018931/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH081884/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH080826/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

