Exercise intolerance
- PMID: 21803233
- PMCID: PMC3694583
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccl.2011.06.002
Exercise intolerance
Abstract
Exercise intolerance is the primary symptom of chronic diastolic heart failure. It is part of the definition of heart failure and is intimately linked to its pathophysiology. Further, exercise intolerance affects the diagnosis and prognosis of heart failure. In addition, understanding the mechanisms of exercise intolerance can lead to developing and testing rational treatments for heart failure. This article focuses on the fundamental principles of exercise physiology and on the assessment, pathophysiology, and potential treatment of exercise intolerance in diastolic heart failure.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
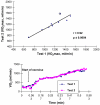


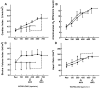
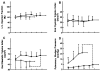
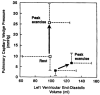

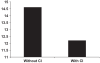
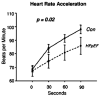


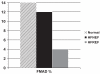

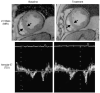
Republished from
-
Exercise intolerance.Heart Fail Clin. 2008 Jan;4(1):99-115. doi: 10.1016/j.hfc.2007.12.002. Heart Fail Clin. 2008. PMID: 18313628 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gandhi SK, Powers JE, Fowle KM, et al. The pathogenesis of acute pulmonary edema associated with hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2000;344(1):17–22. - PubMed
-
- Powers JE, Gandhi SK, Kramer RK, et al. Predictors of poor outcome in patients with hypertensivepulmonary edema [abstract] J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;43(5A):227A.
-
- Kitzman DW, Little WC, Brubaker PH, et al. Pathophysiological characterization of isolated diastolic heart failure in comparison to systolic heart failure. JAMA. 2002;288(17):2144–50. - PubMed
-
- Bol E, de Vries WR, Mosterd WL, et al. Cardiopulmonary exercise parameters in relation to all-cause mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. Int J Cardiol. 2000;72:255–63. - PubMed
-
- Jones RC, Francis GS, Lauer MS. Predictors of mortality in patients with heart failure and preserved systolic function in the Digitalis Investigation Group trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44(5):1025–9. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

