Deletion of the mammalian INDY homolog mimics aspects of dietary restriction and protects against adiposity and insulin resistance in mice
- PMID: 21803289
- PMCID: PMC3163140
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.06.009
Deletion of the mammalian INDY homolog mimics aspects of dietary restriction and protects against adiposity and insulin resistance in mice
Erratum in
- Cell Metab. 2011 Oct 5;14(4):567
Abstract
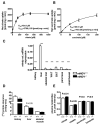
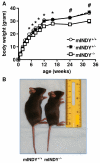
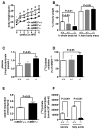
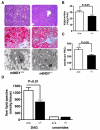
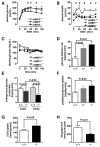
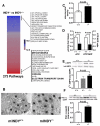
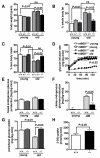
Reduced expression of the Indy (I'm Not Dead, Yet) gene in D. melanogaster and its homolog in C. elegans prolongs life span and in D. melanogaster augments mitochondrial biogenesis in a manner akin to caloric restriction. However, the cellular mechanism by which Indy does this is unknown. Here, we report on the knockout mouse model of the mammalian Indy (mIndy) homolog, SLC13A5. Deletion of mIndy in mice (mINDY(-/-) mice) reduces hepatocellular ATP/ADP ratio, activates hepatic AMPK, induces PGC-1α, inhibits ACC-2, and reduces SREBP-1c levels. This signaling network promotes hepatic mitochondrial biogenesis, lipid oxidation, and energy expenditure and attenuates hepatic de novo lipogenesis. Together, these traits protect mINDY(-/-) mice from the adiposity and insulin resistance that evolve with high-fat feeding and aging. Our studies demonstrate a profound effect of mIndy on mammalian energy metabolism and suggest that mINDY might be a therapeutic target for the treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bergeron R, Ren JM, Cadman KS, Moore IK, Perret P, Pypaert M, Young LH, Semenkovich CF, Shulman GI. Chronic activation of AMP kinase results in NRF-1 activation and mitochondrial biogenesis. Am. J. Physiol Endocrinol. Metab. 2001;281:E1340–E1346. - PubMed
-
- Bosca L, Aragon JJ, Sols A. Modulation of muscle phosphofructokinase at physiological concentration of enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1985;260:2100–2107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 DK-40936/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK-59635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG-16667/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059635/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK-45735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK045735/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK-034989/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034989/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG016667/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK040936/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG024353/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK085638/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023686/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

